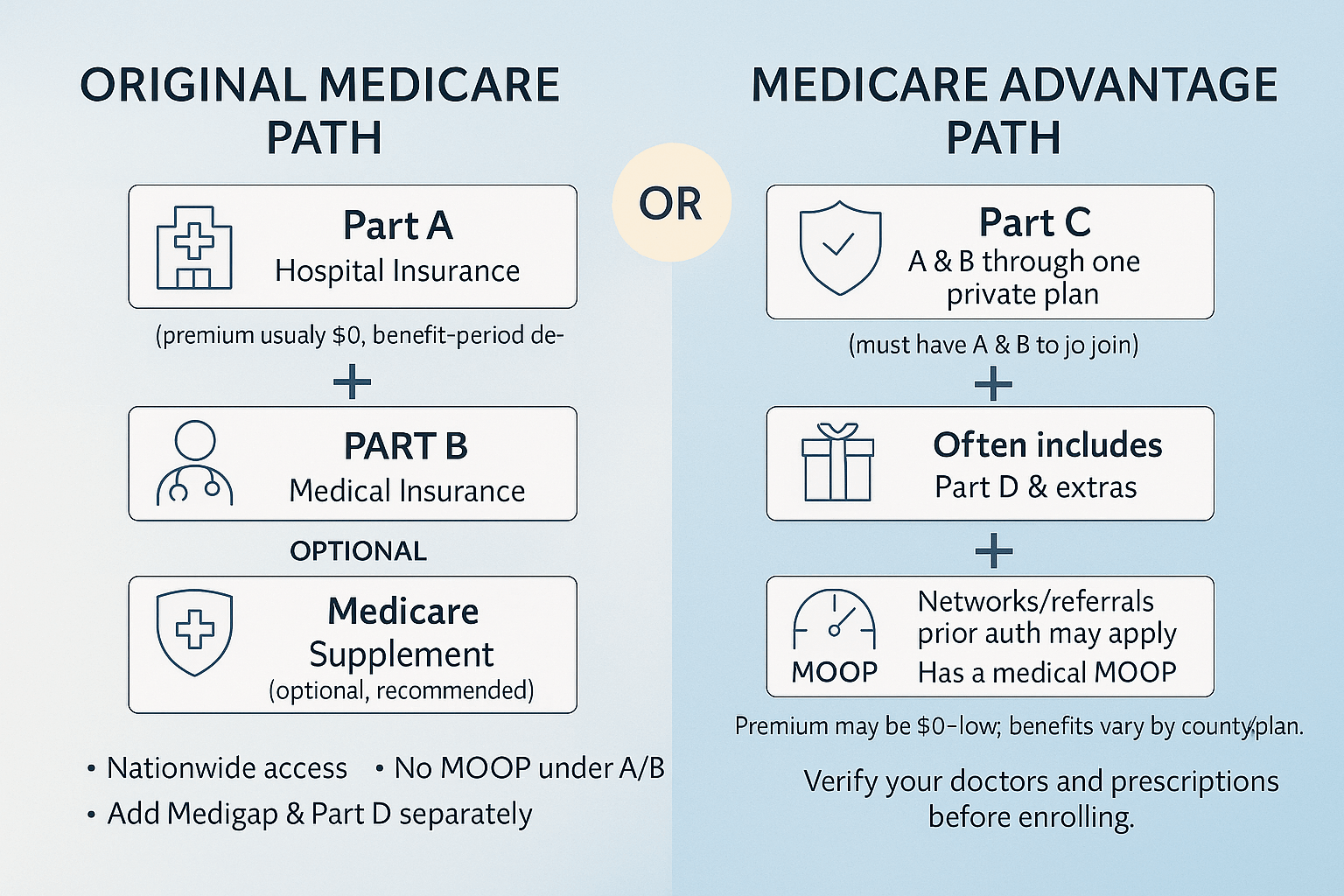
| Stays on Original Medicare (A & B). Medigap pays some/all Medicare cost-shares. Separate Part D plan for drugs. | How it works | Private plan replaces Original Medicare for most services; follows plan rules and networks. Many include Part D. |
| Usually higher premiums (Medigap + Part D). | Monthly cost | Usually lower premiums (often $0–low), single card. |
| Very predictable/low with richer Medigap plans (e.g., G, N). No MA MOOP applies; you pay Medicare + Medigap rules only. | Out-of-pocket risk | Capped by an annual in-network MOOP (but can be several thousand dollars). Costs vary by service and network. |
| Any doctor/hospital that takes Medicare nationwide—no referrals, no network. Great for travel/snowbirds. | Provider access | Networks (HMO/PPO). Some require referrals/authorizations. Out-of-network may cost more or not be covered. |
| Separate Part D (choose the one that fits meds). | Drug coverage | Often built-in Part D (MAPD); must follow plan’s formulary. |
| Typically not included (may buy stand-alone add-ons). | Extras (dental/vision/OTC, gym) | Often included or offered as riders (varies by plan). |
| Minimal plan management; Medicare rules apply. | Care management | More care coordination (prior authorization, step therapy possible). |
| Strong—Medicare nationwide + Medigap. Foreign travel limited (only some plans offer small emergency benefit). | Travel / living in multiple states | Mixed—Emergencies covered; routine care limited to network/service area (PPOs more flexible than HMOs). |
| People who value maximum choice, predictability, and travel flexibility. | Best for | People who prefer lower premiums, bundled benefits, and can use provider networks. |
- Widest provider choice (any Medicare provider).
- Very predictable costs with Plan G/N.
- Strong for frequent travelers/snowbirds.
- No referrals, minimal prior authorization.
| Pros |
- Low/zero premiums common.
- Bundled extras (dental/vision/hearing, OTC, fitness).
- Annual chance to change plans without health questions.
- In-network MOOP limits worst-case costs.
|
- Higher monthly premiums (plus separate Part D)
- Dental/vision/OTC typically not included.
- Outside GI periods, Medigap may require underwriting to enroll or upgrade.
| Cons |
- Network rules, possible referrals/prior authorization.
- Cost-sharing can add up when using services.
- Travel/living in multiple states can be tricky.
- Benefits, formularies, and networks can change yearly.
|