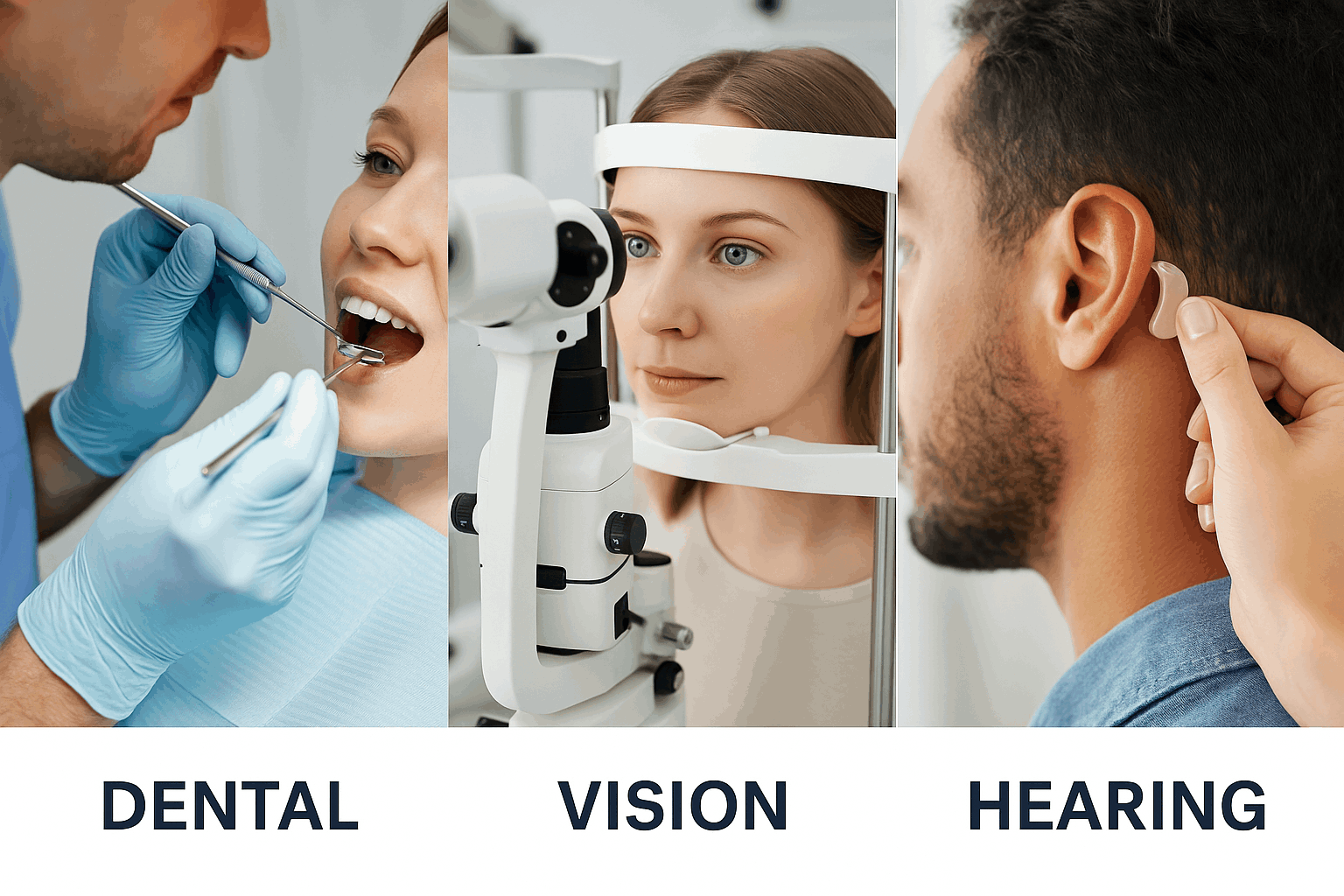
Dental, Vision and Hearing Insurance
Maintaining good oral, visual, and auditory health is essential to your overall well-being. That’s why many insurance plans offer Dental, Vision, and Hearing coverage — three vital components that go beyond standard medical care.
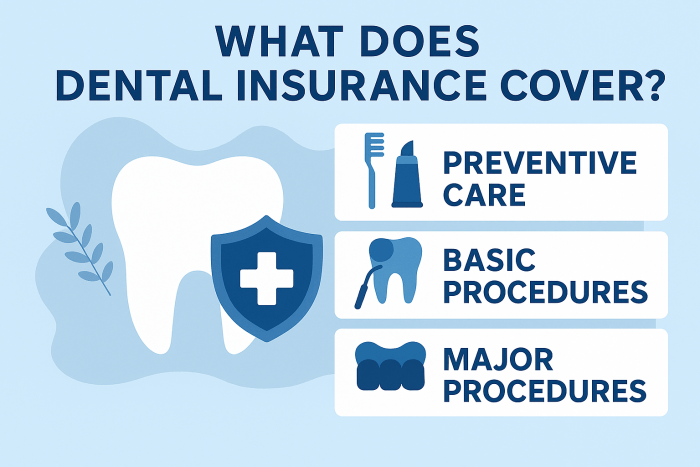
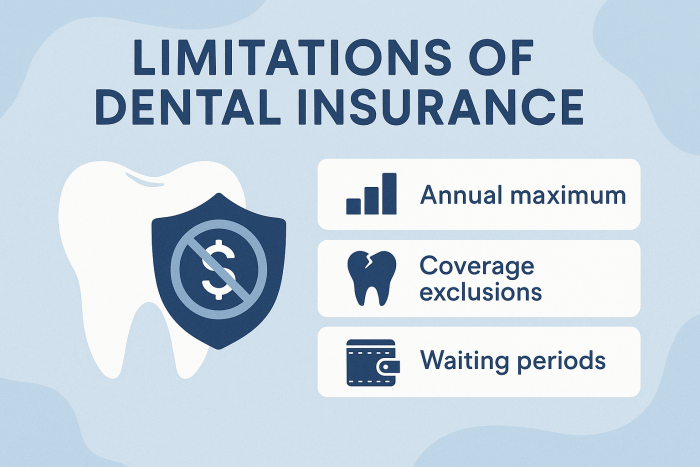
- Dental benefits help you protect your smile through preventive services, routine check-ups, and treatment for dental issues before they become serious.
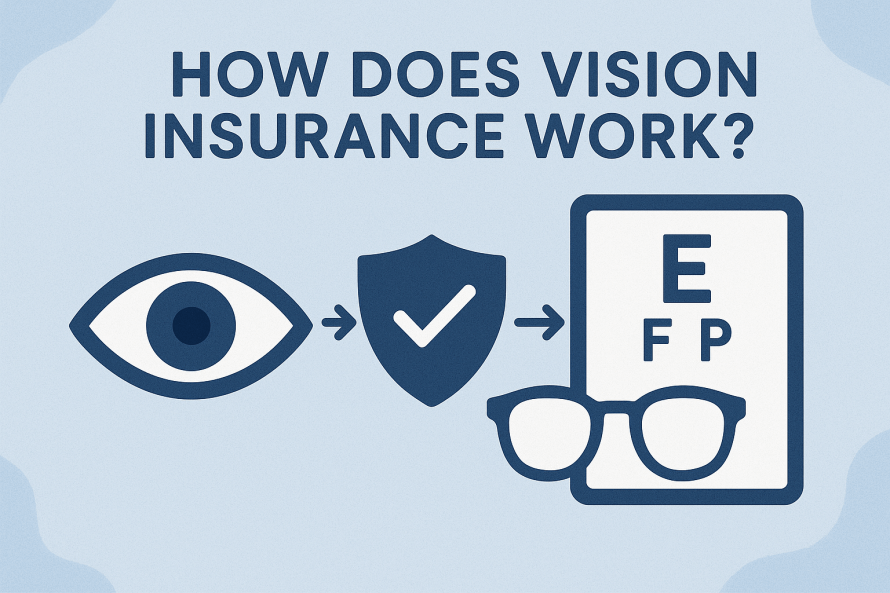
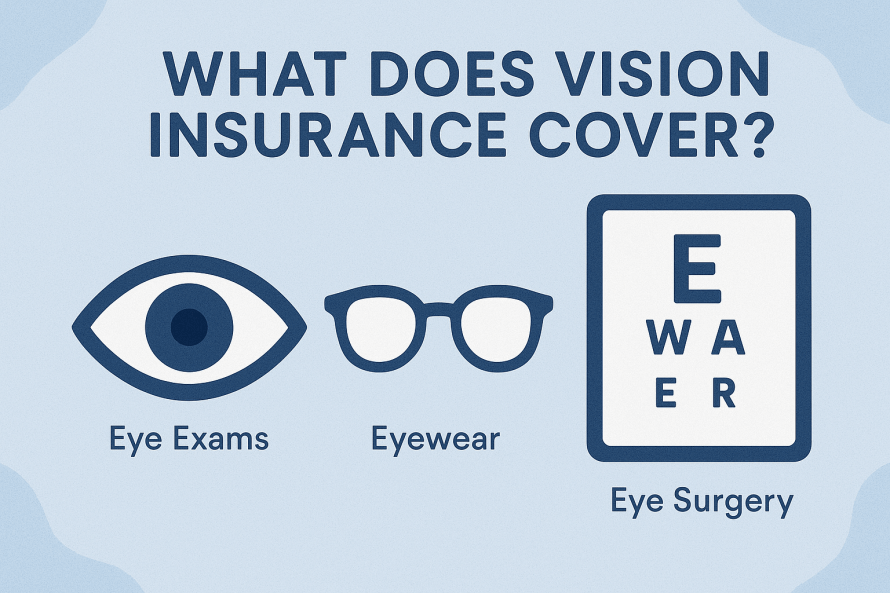
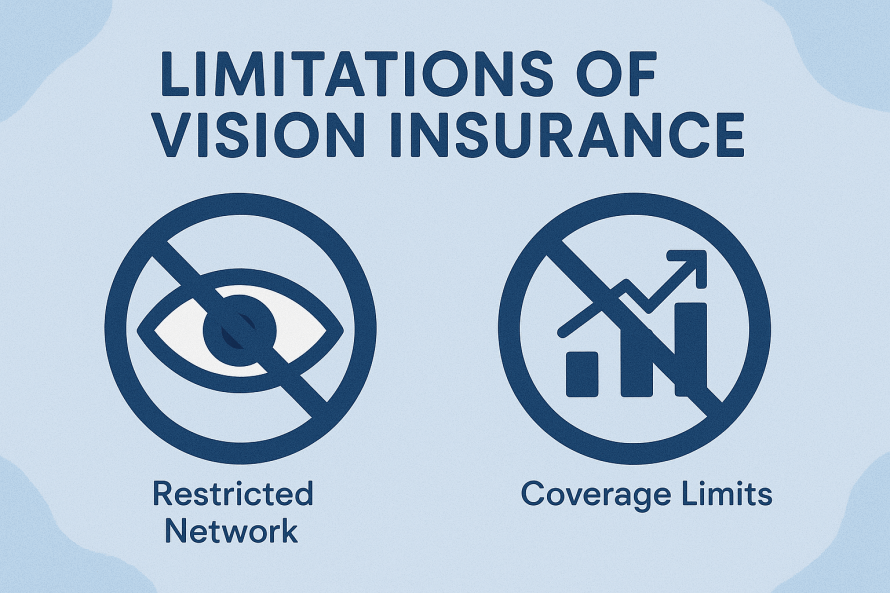
- Vision benefits ensure you have access to regular eye exams, corrective lenses, and early detection of eye diseases to preserve clear, healthy sight.
- Hearing benefits provide coverage for hearing exams, hearing aids, and related services to keep you connected and engaged with the world around you.
Together, these benefits support your long-term health, quality of life, and confidence, helping you see, hear, and smile with ease