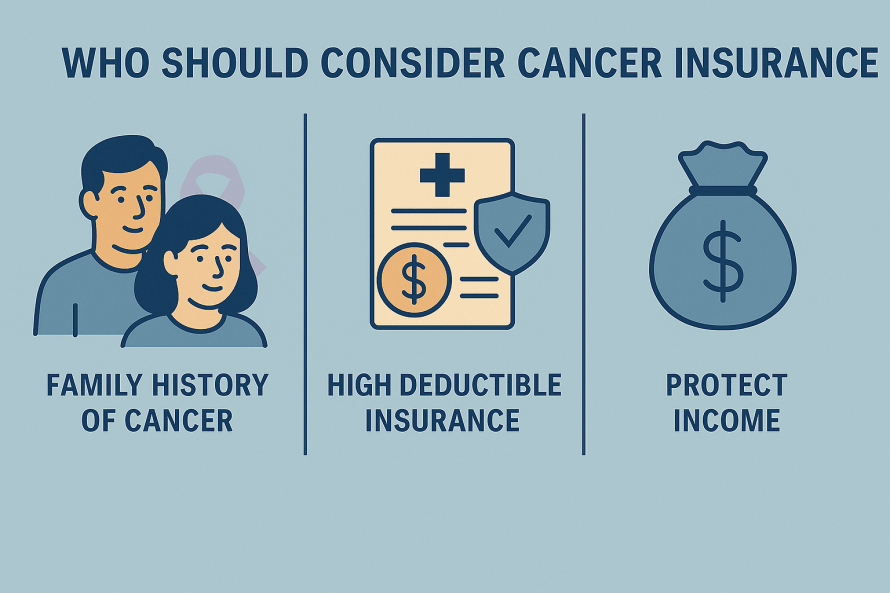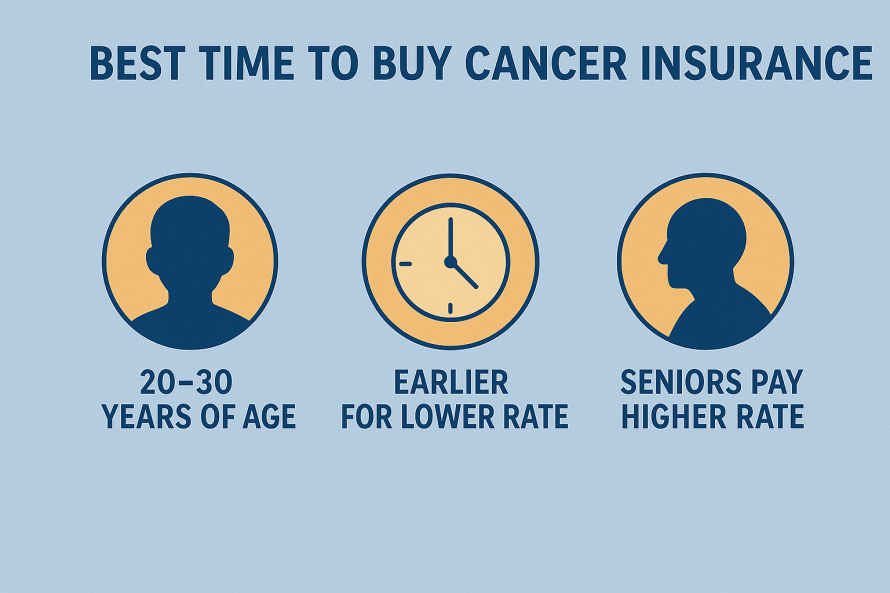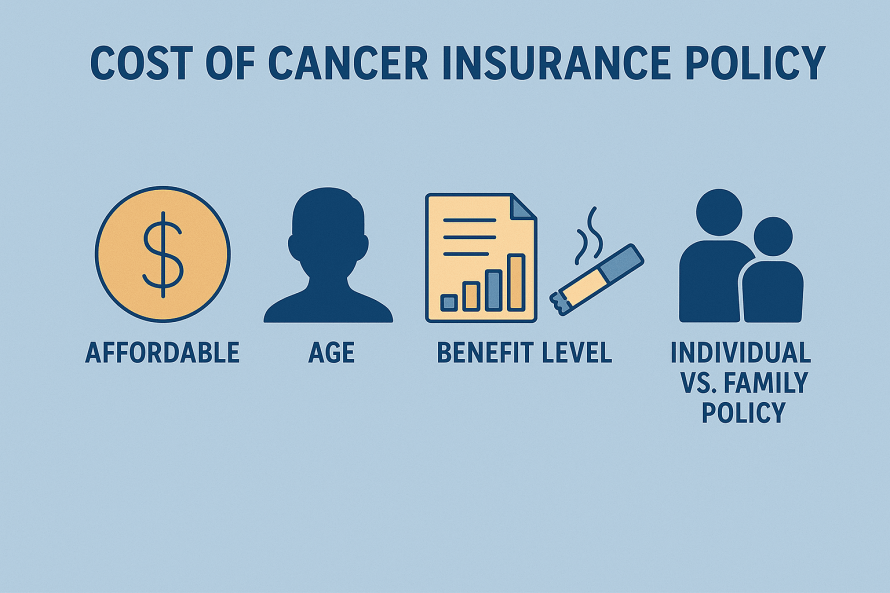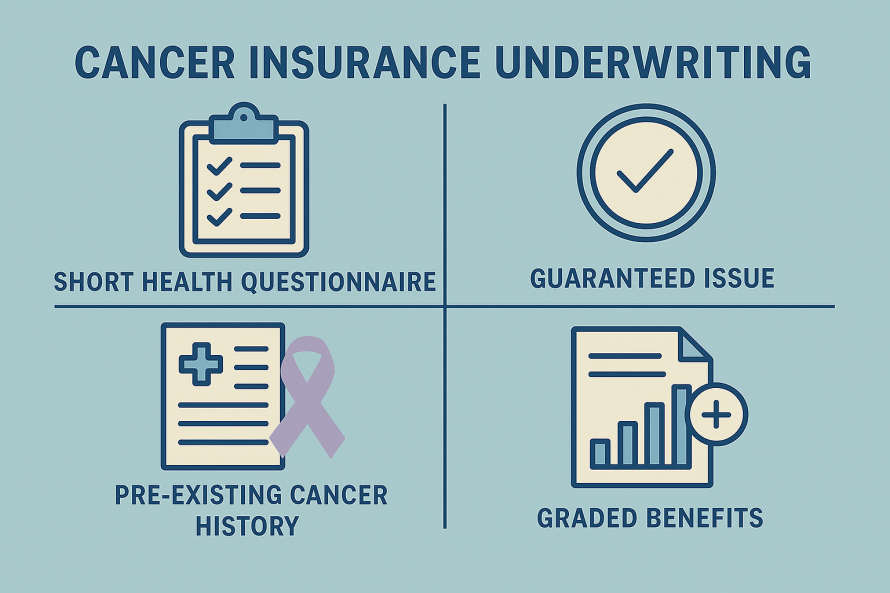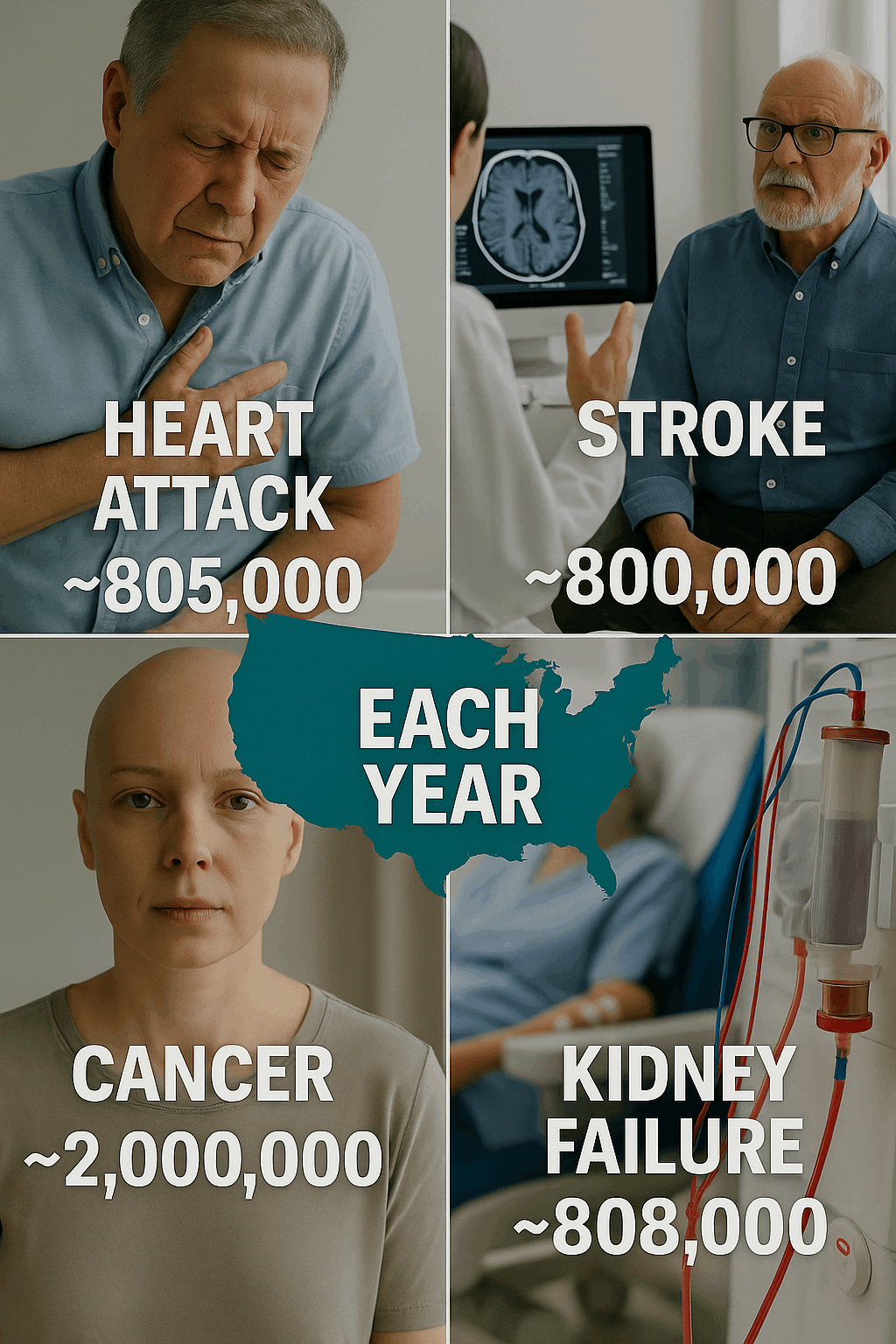
Critical Illness Insurance
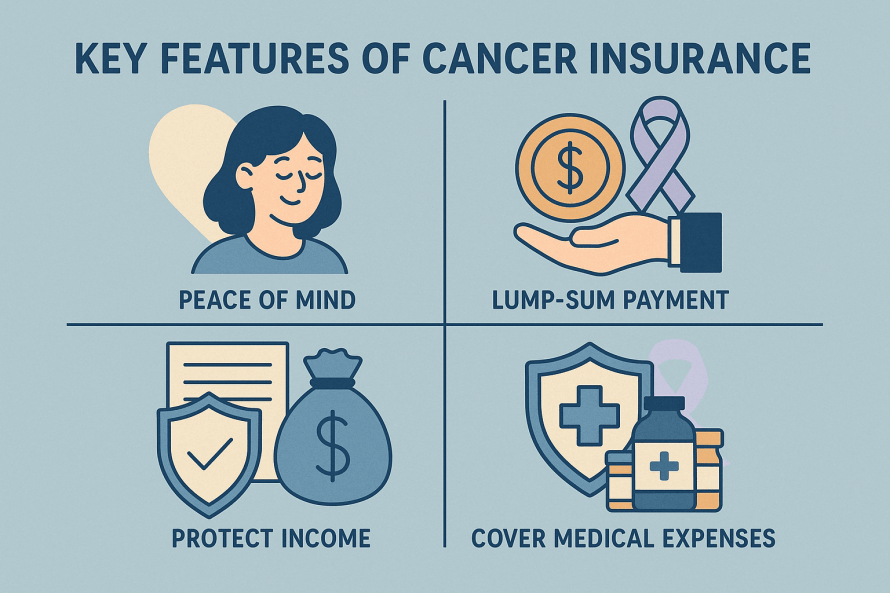
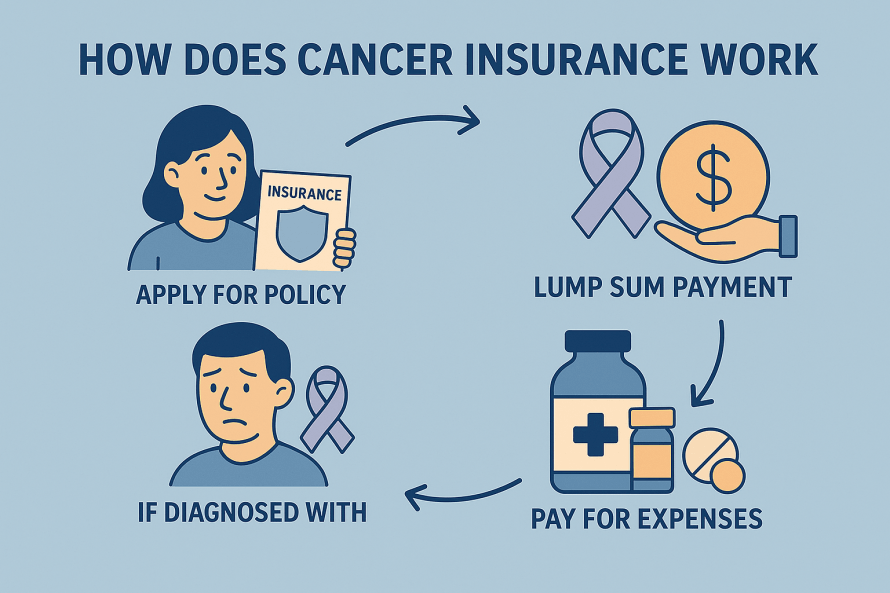
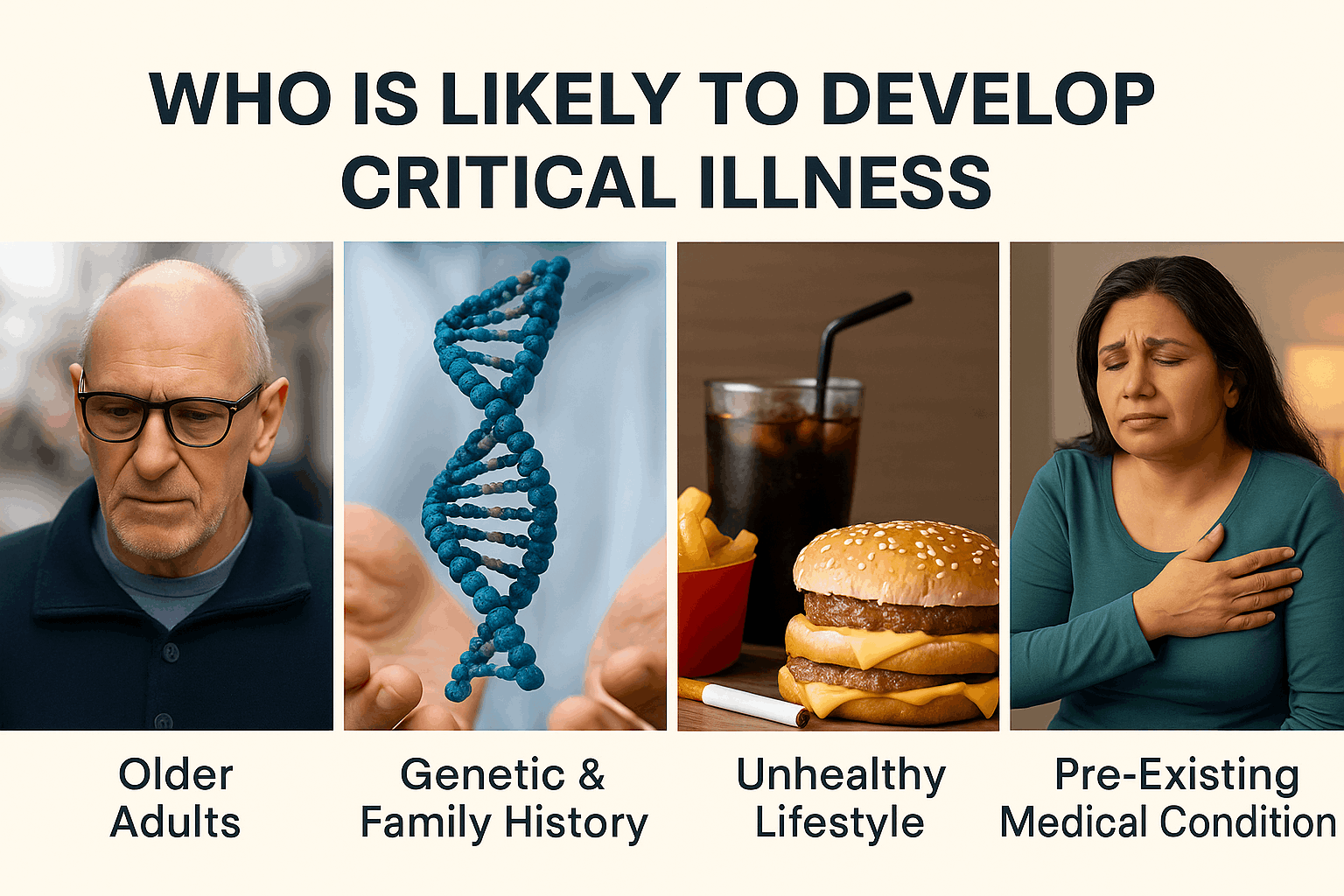
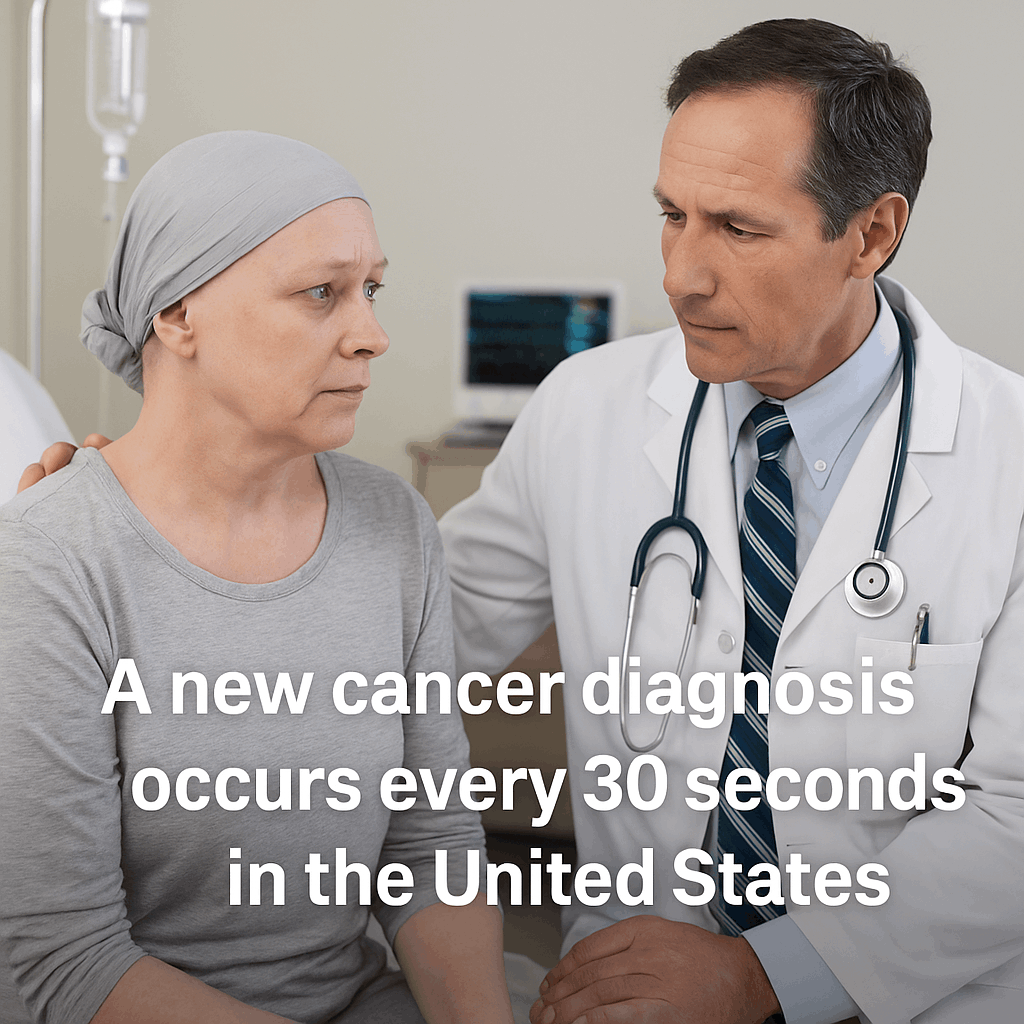
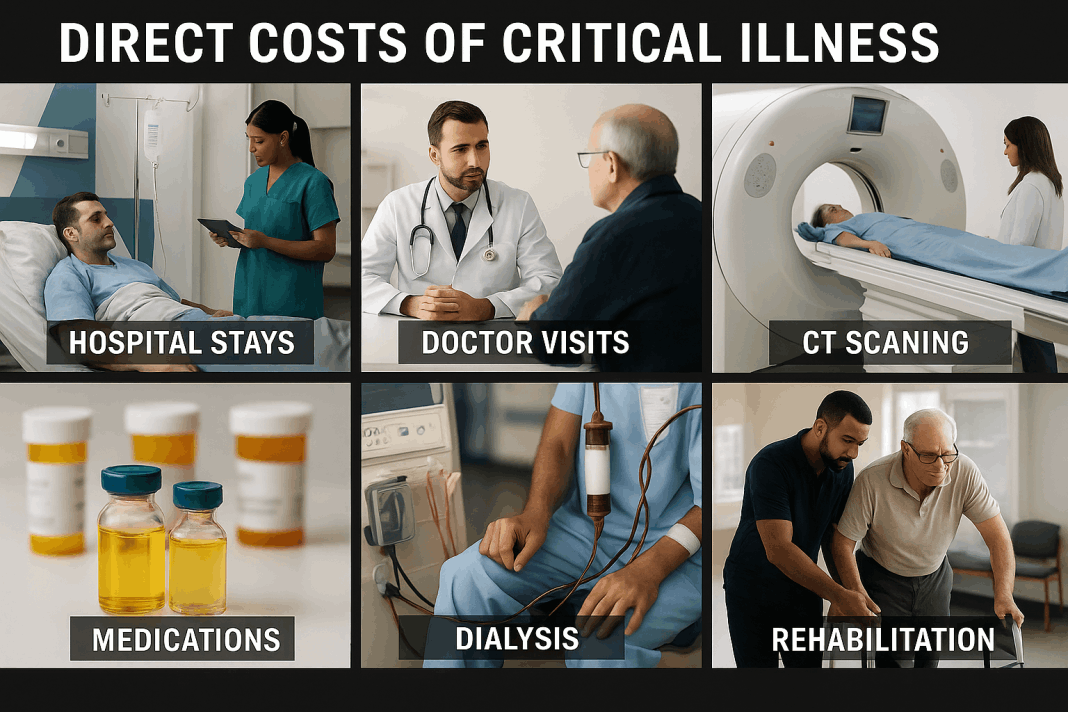
Critical Illness Insurance is a type of insurance policy that provides a lump-sum cash benefit if you are diagnosed with a covered serious illness such as heart attack, stroke, cancer, kidney failure, or major organ transplant.
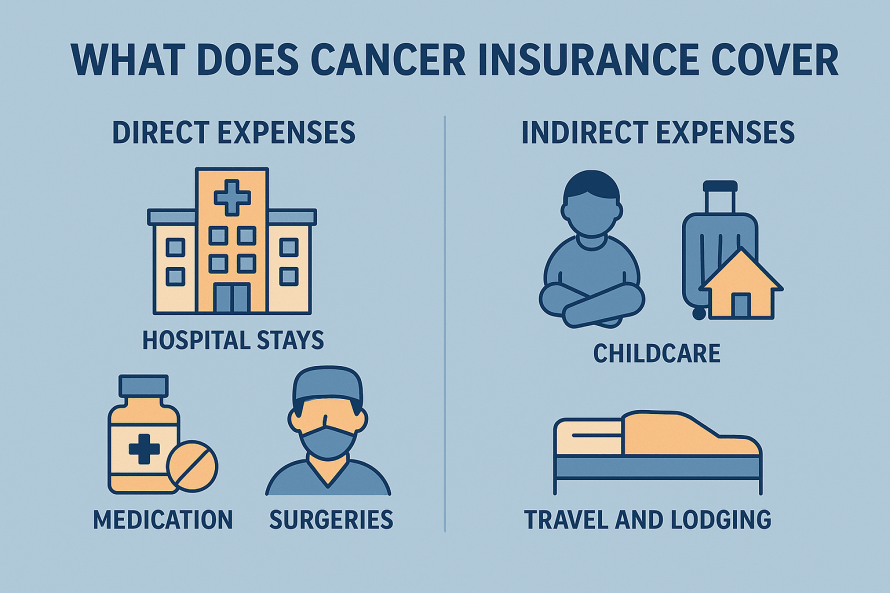
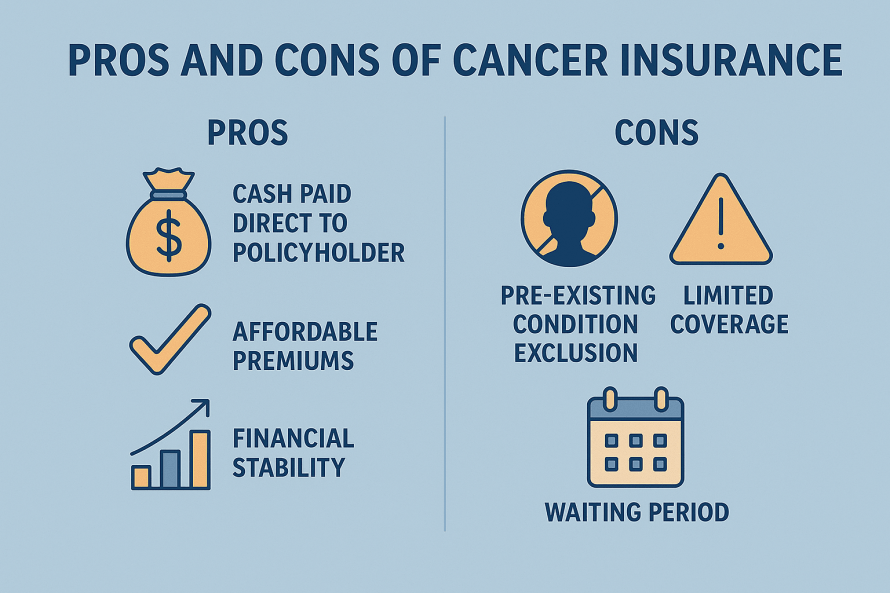
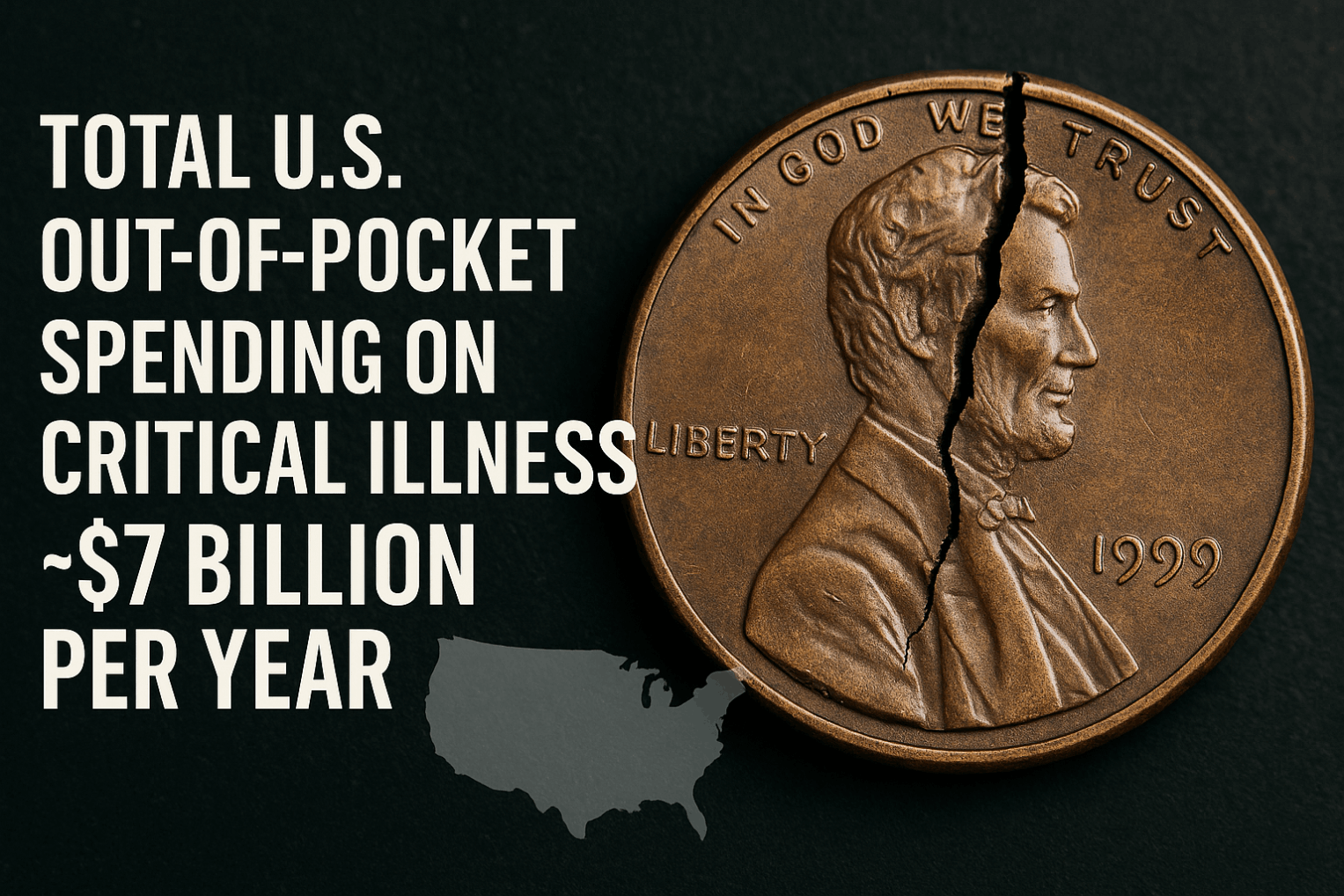
Unlike health insurance, which pays doctors and hospitals directly, the benefit from Critical Illness Insurance is paid directly to you. This money can be used however you need — for medical expenses, mortgage payments, household bills, travel for treatment, childcare, or even income replacement while you recover.
Its main purpose is to ease the financial burden that comes with life-threatening conditions, so you and your family can focus on recovery rather than money worries.