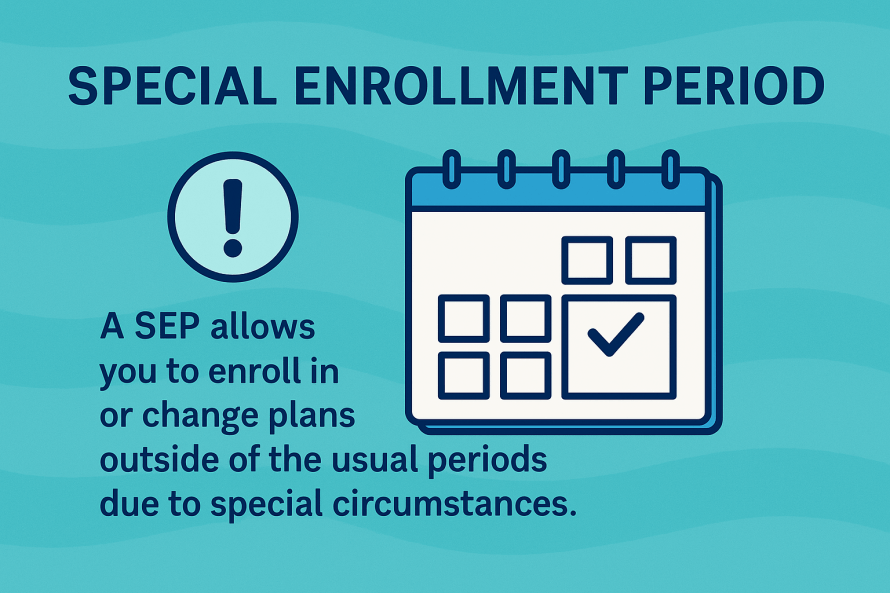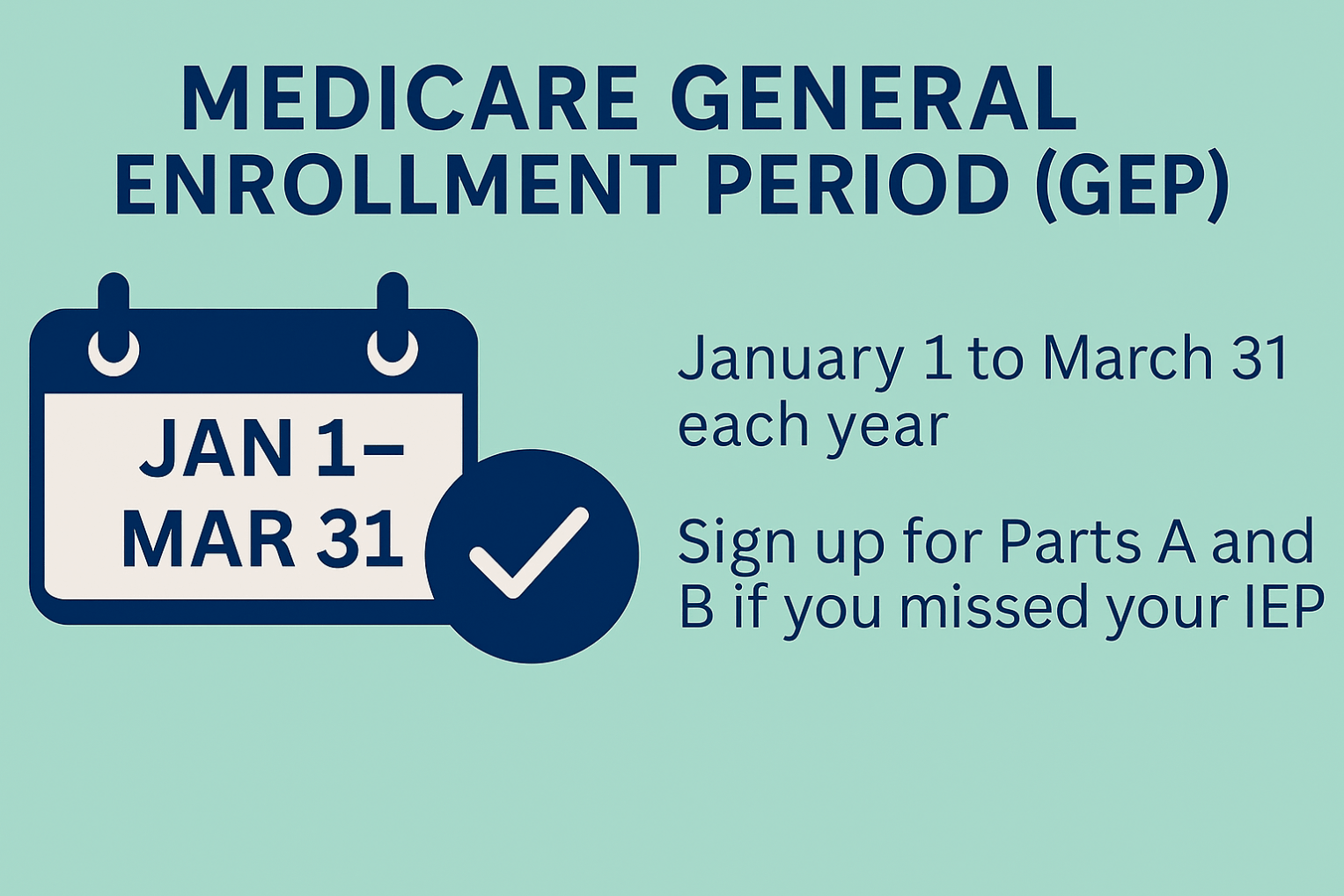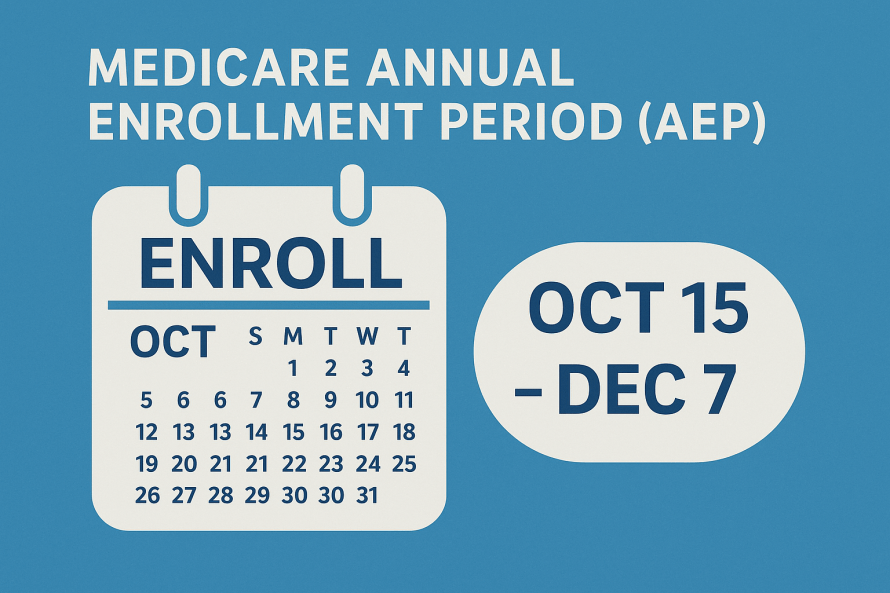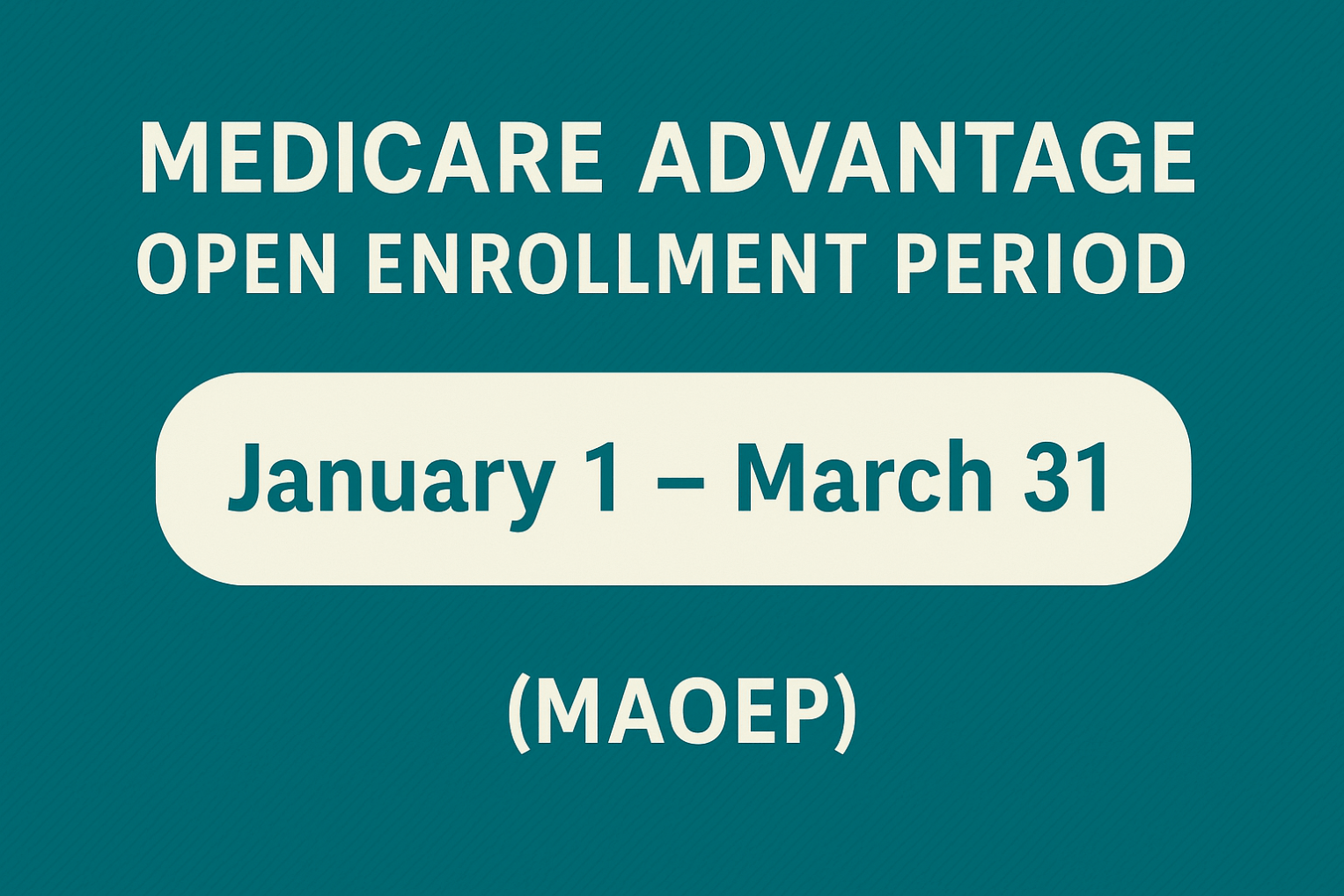
Medicare Basics
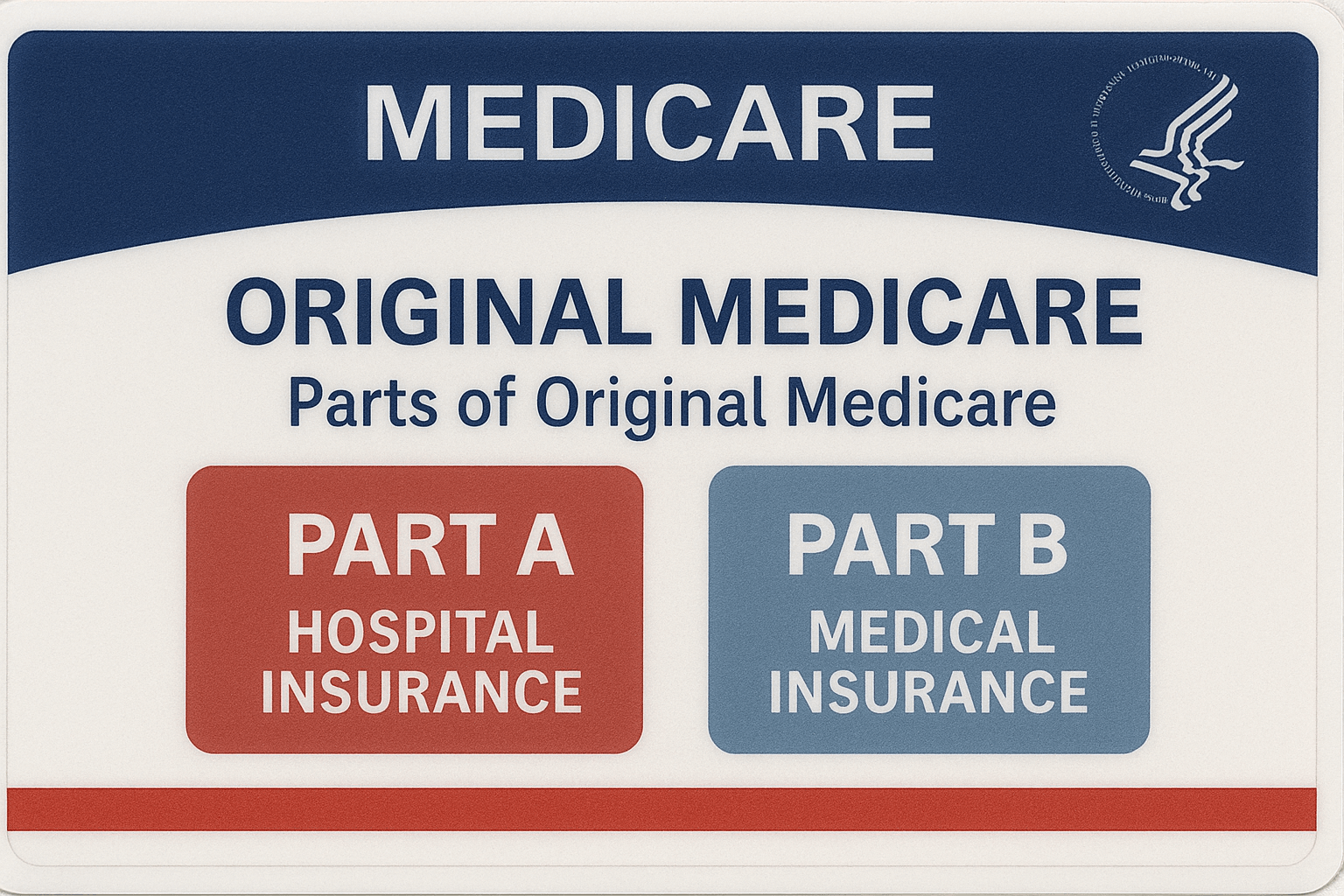
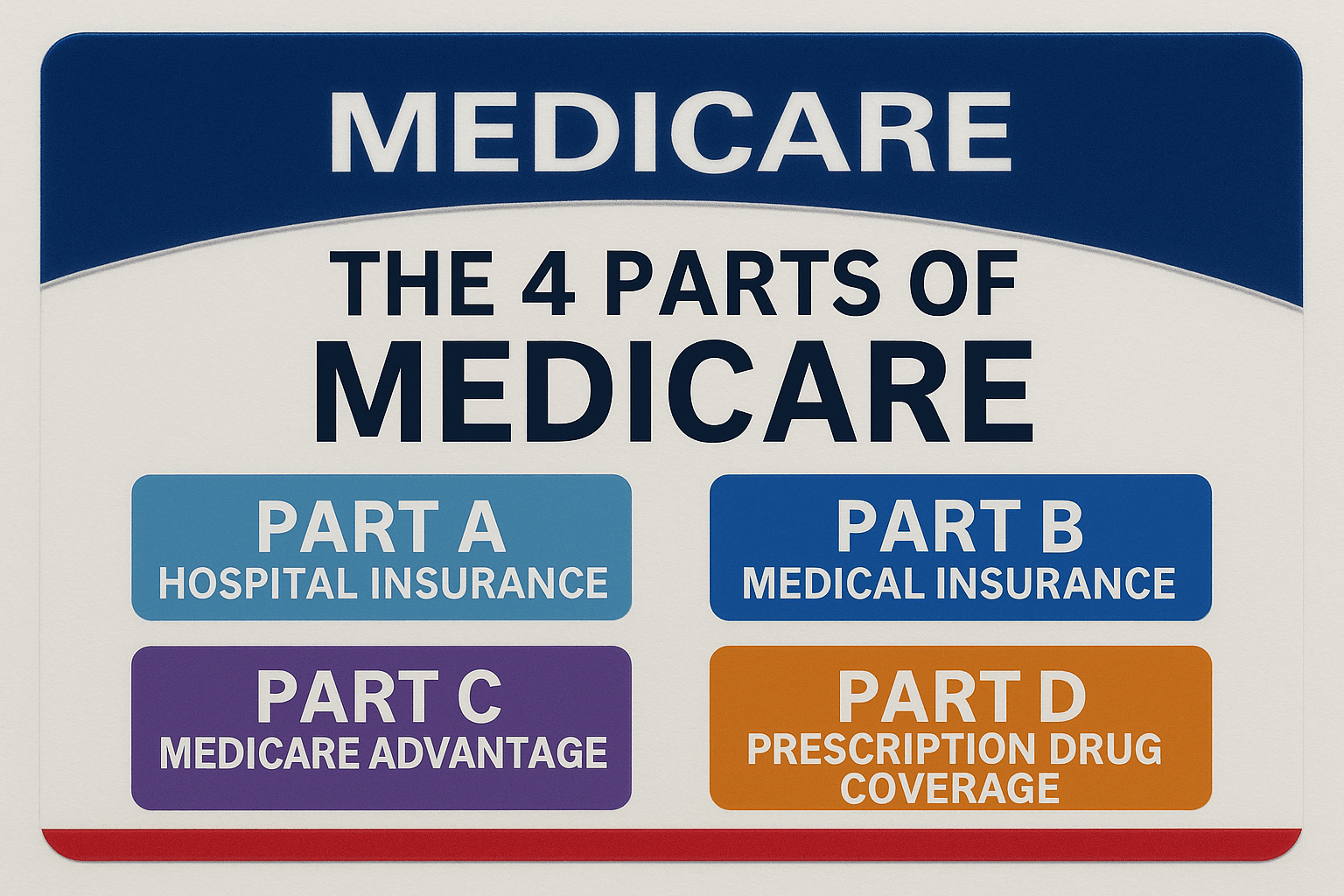
Medicare is a federal health insurance program in the United States designed primarily for individuals aged 65 and older, although it also provides coverage for certain younger people with disabilities and those with End-Stage Renal Disease (permanent kidney failure requiring dialysis or a transplant). Established in 1965 under the Social Security Act, Medicare helps cover many essential medical services, including hospital care, doctor visits, preventive services, and prescription drugs. The program is divided into four parts: Part A covers inpatient hospital care, skilled nursing facility care, hospice, and some home health services; Part B helps cover outpatient care such as doctor visits, lab tests, and preventive services; Part C, also known as Medicare Advantage, is an alternative way to receive Medicare benefits through private insurance plans approved by Medicare that often include additional services like vision, dental, or hearing coverage; and Part D provides prescription drug coverage through private plans. While Medicare helps reduce healthcare costs, it does not cover all expenses, and many beneficiaries choose to enroll in supplemental insurance plans to help pay for deductibles, copayments, and other out-of-pocket costs.