Special Needs Plans (SNPs)
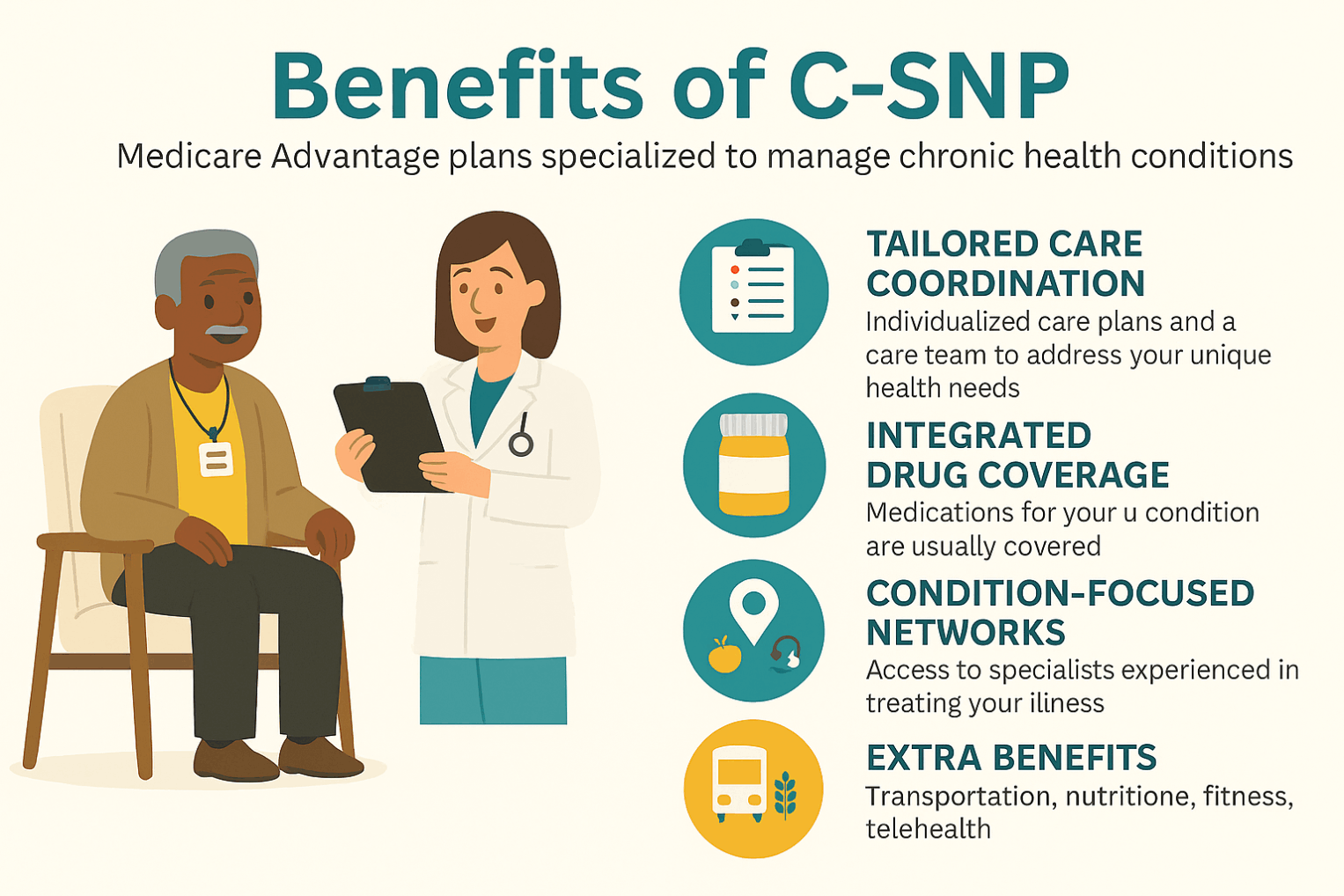
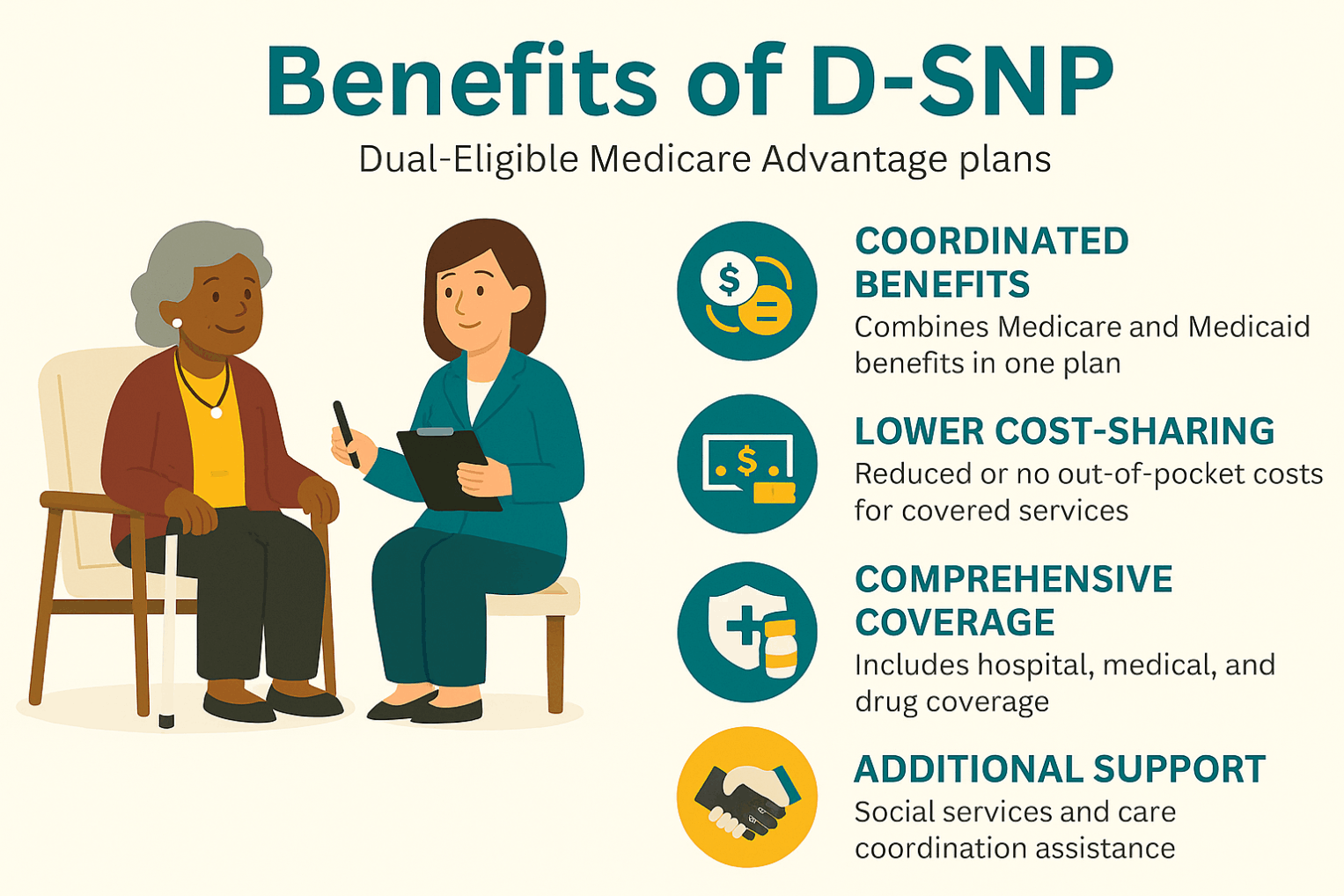
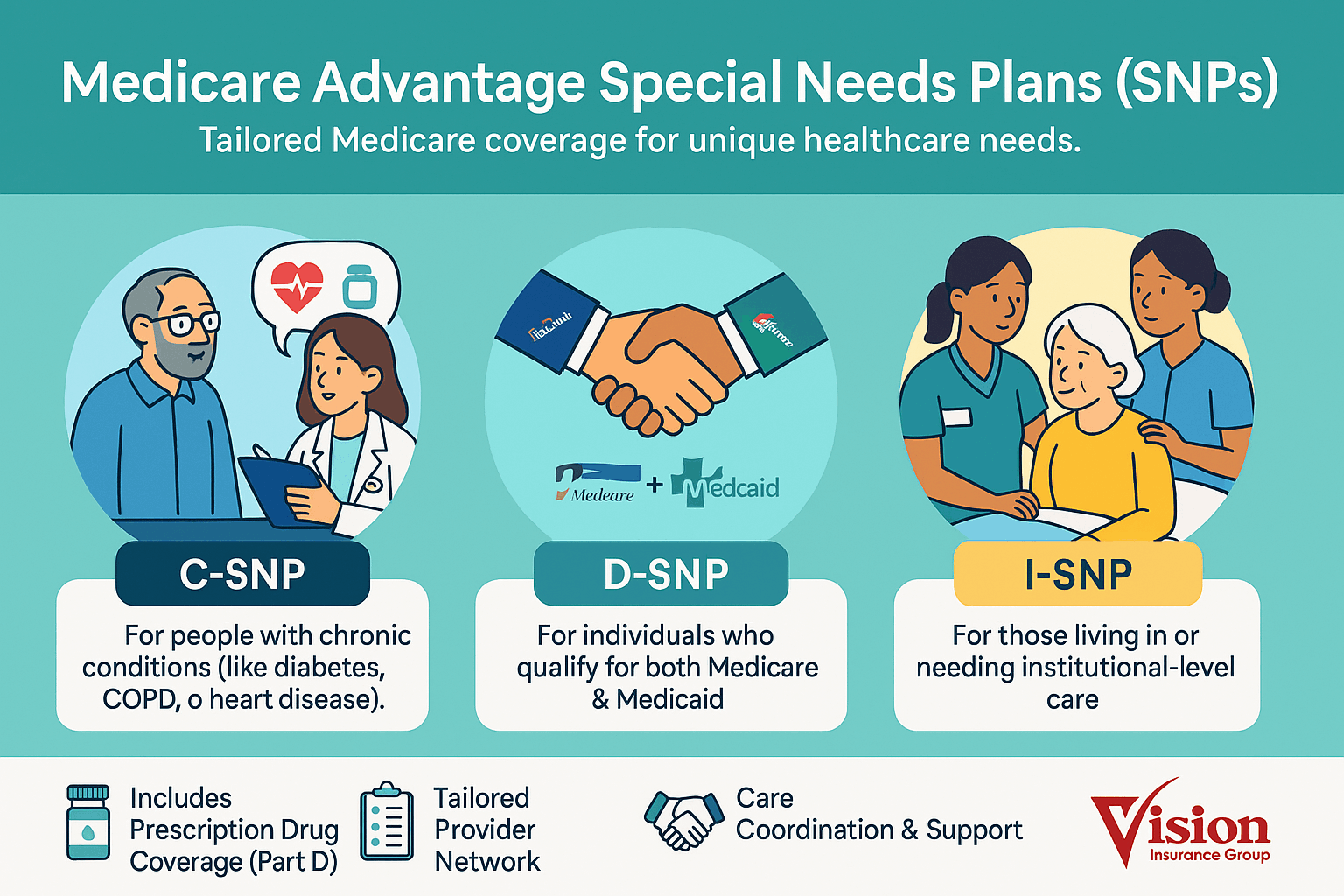
Special Needs Plans (SNPs) are Medicare Advantage (Part C) plans tailored for people with specific circumstances or health needs. They provide all Part A and Part B benefits and usually include Part D drug coverage, plus a coordinated Model of Care (care team, individualized care plans, and targeted benefits).
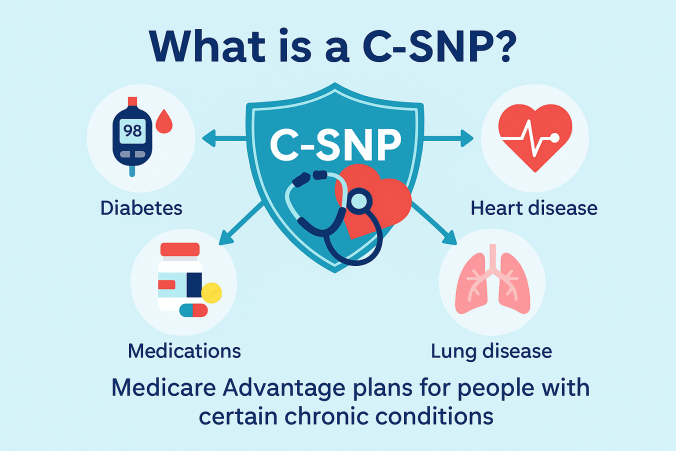
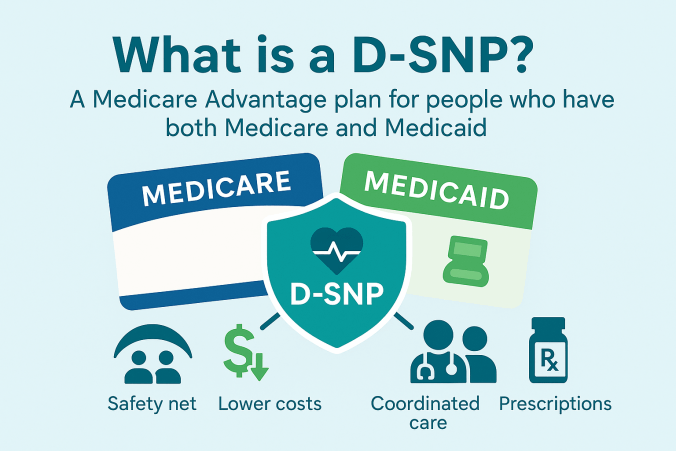
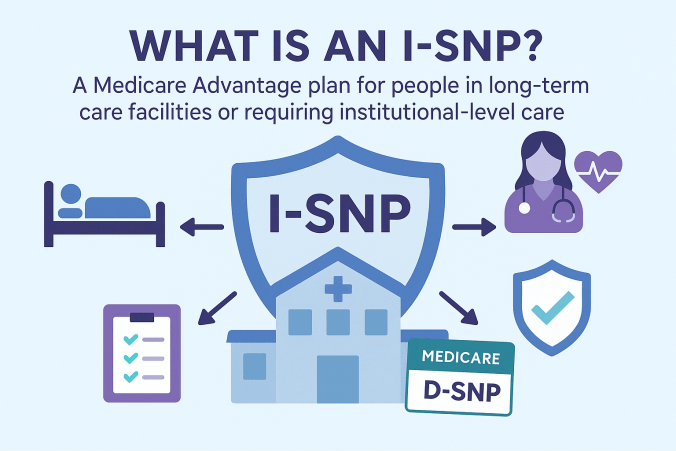
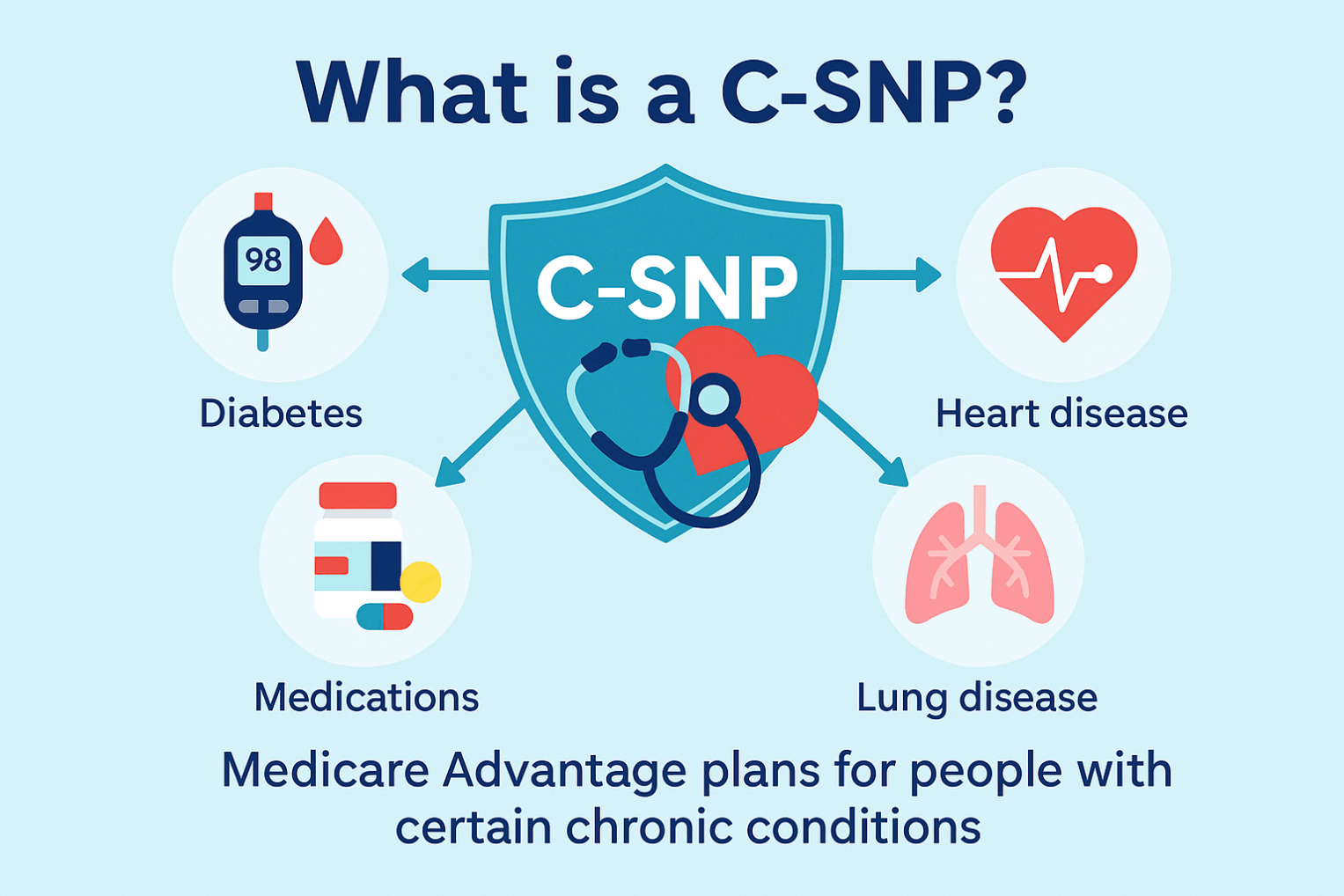
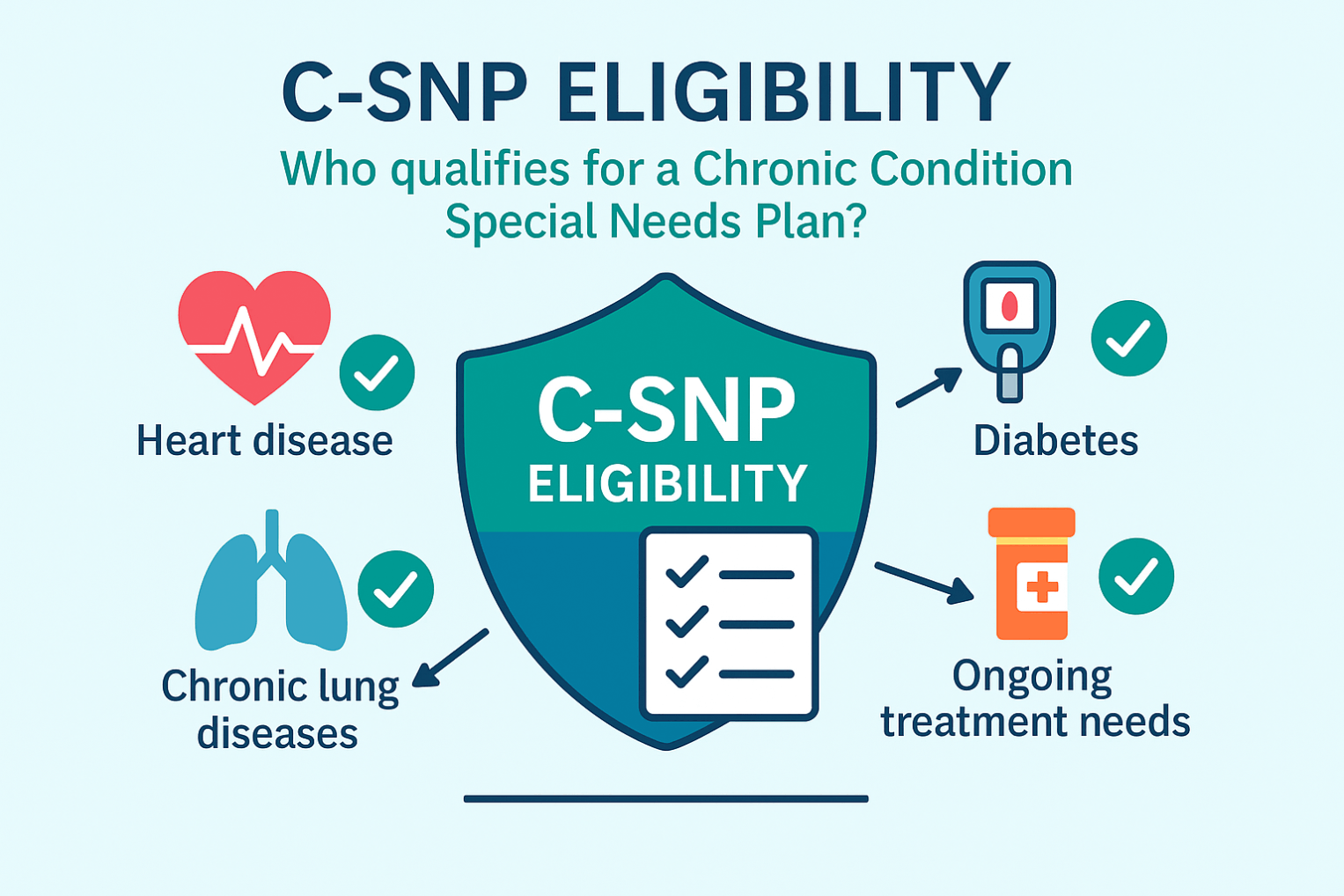
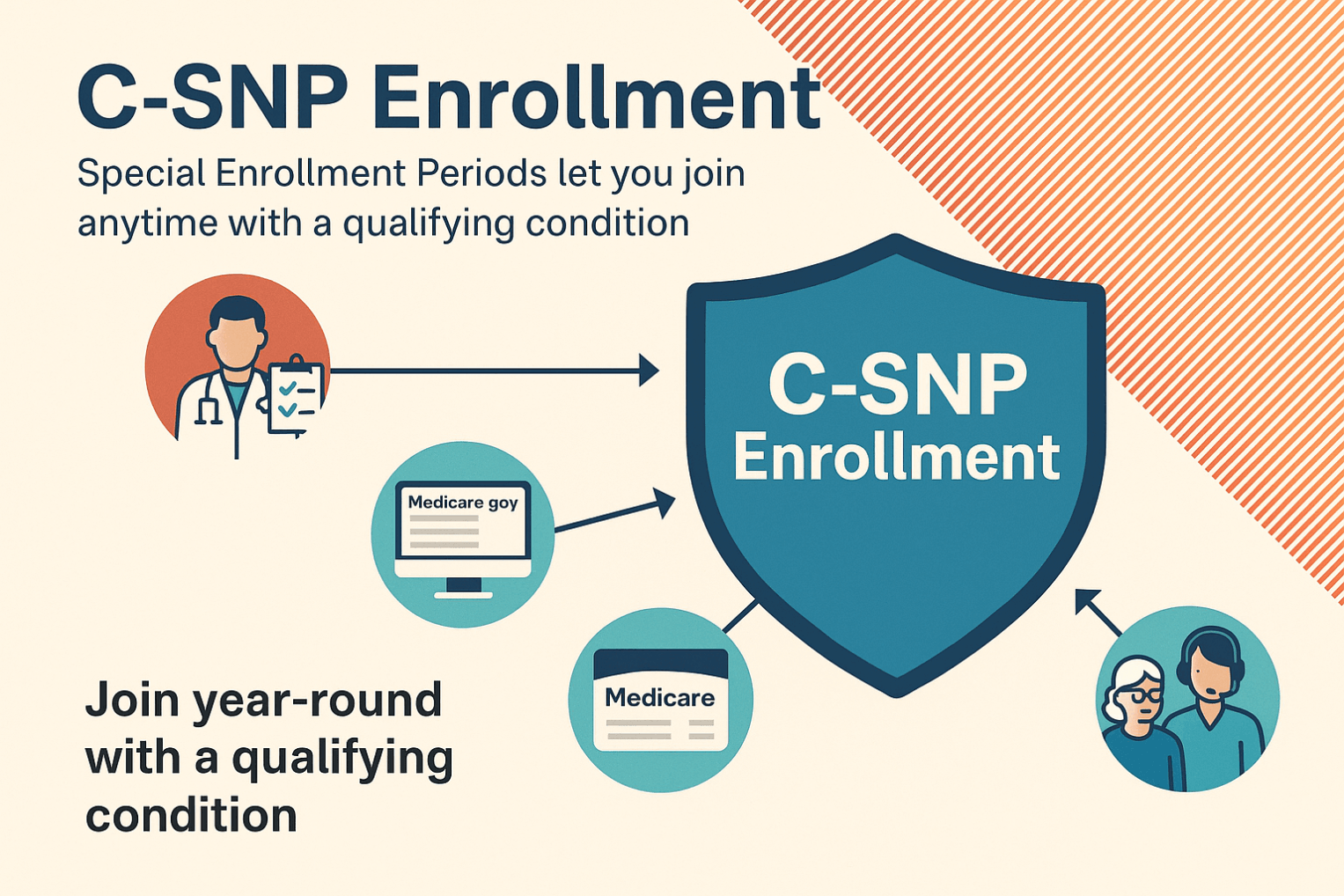
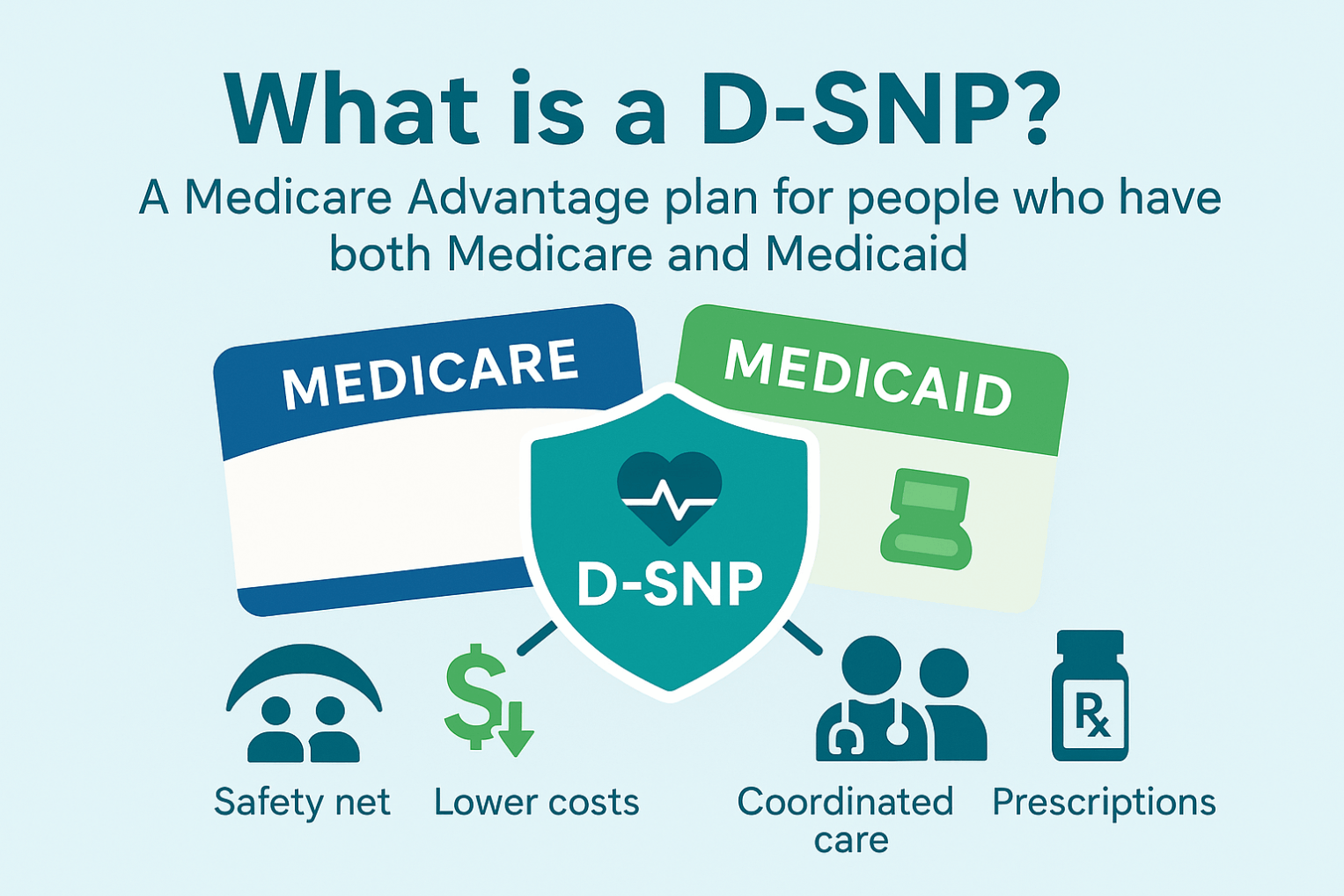
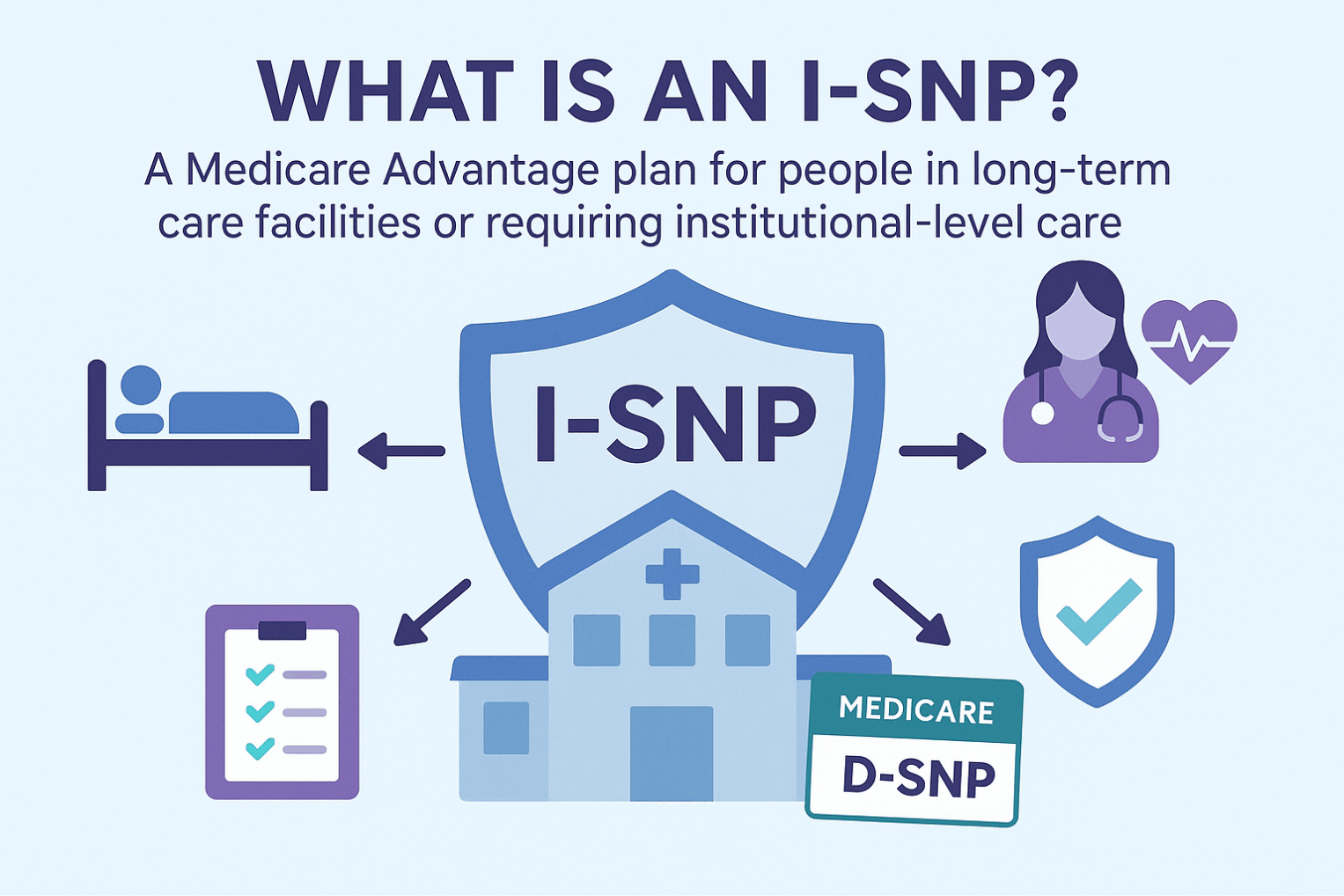
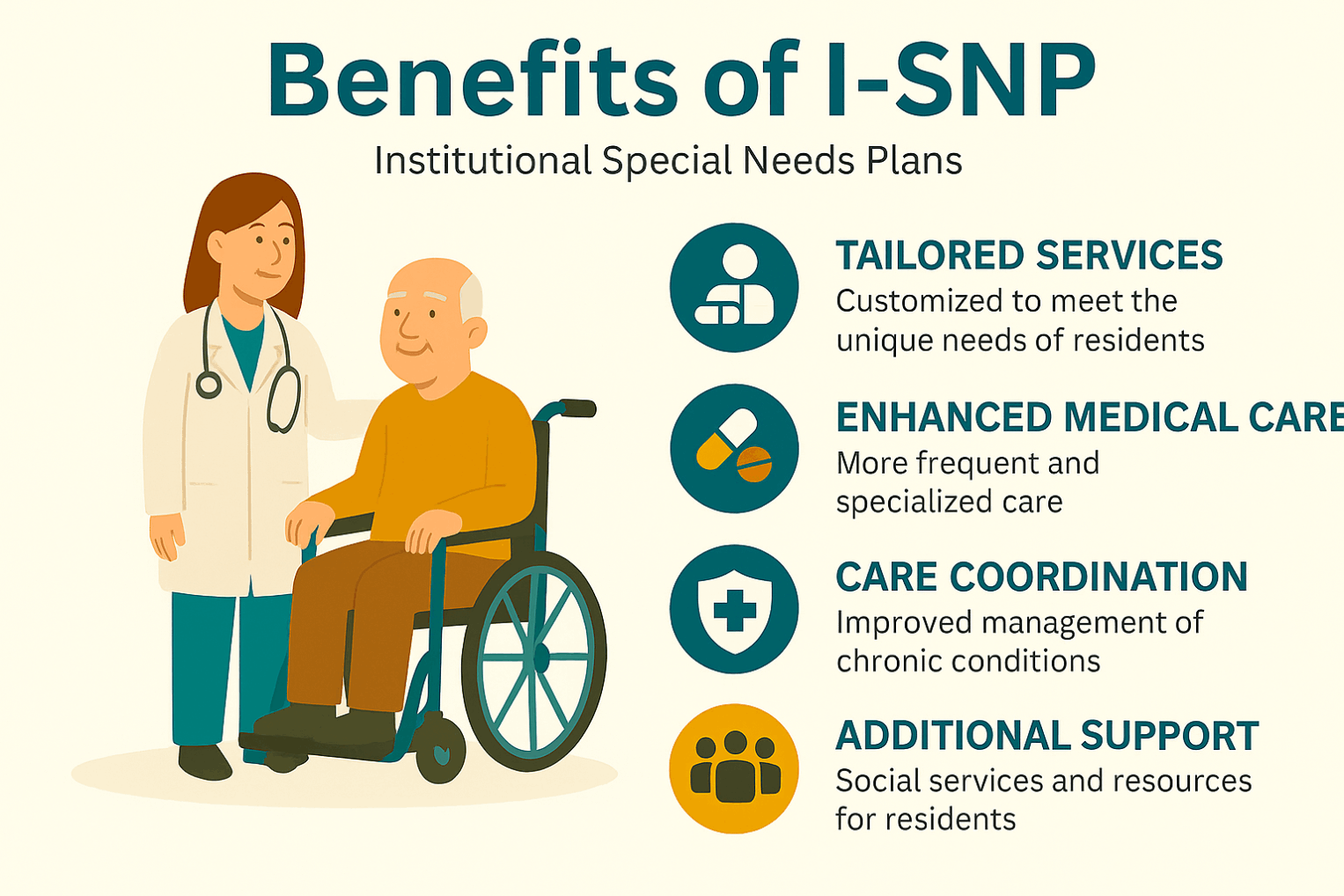
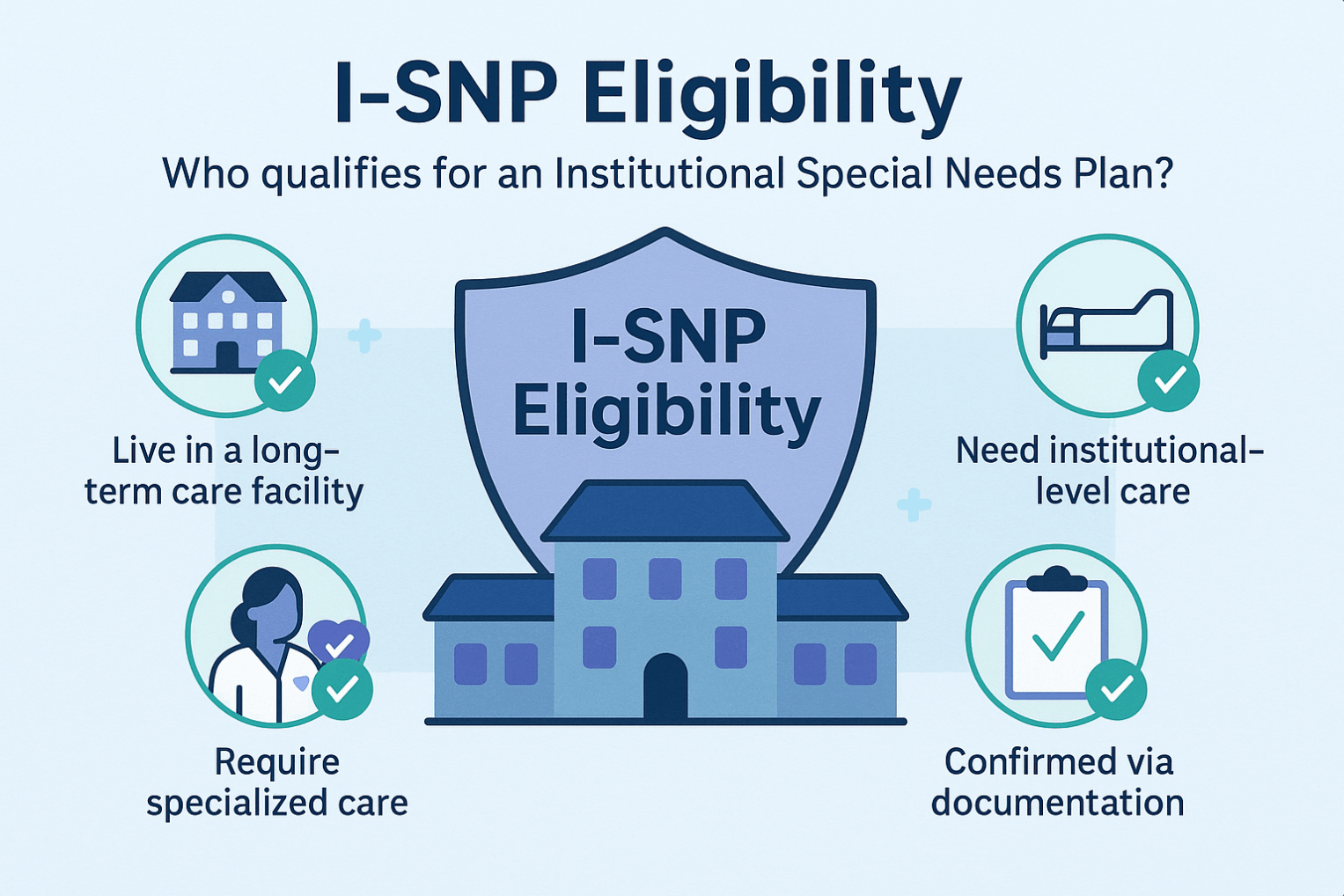
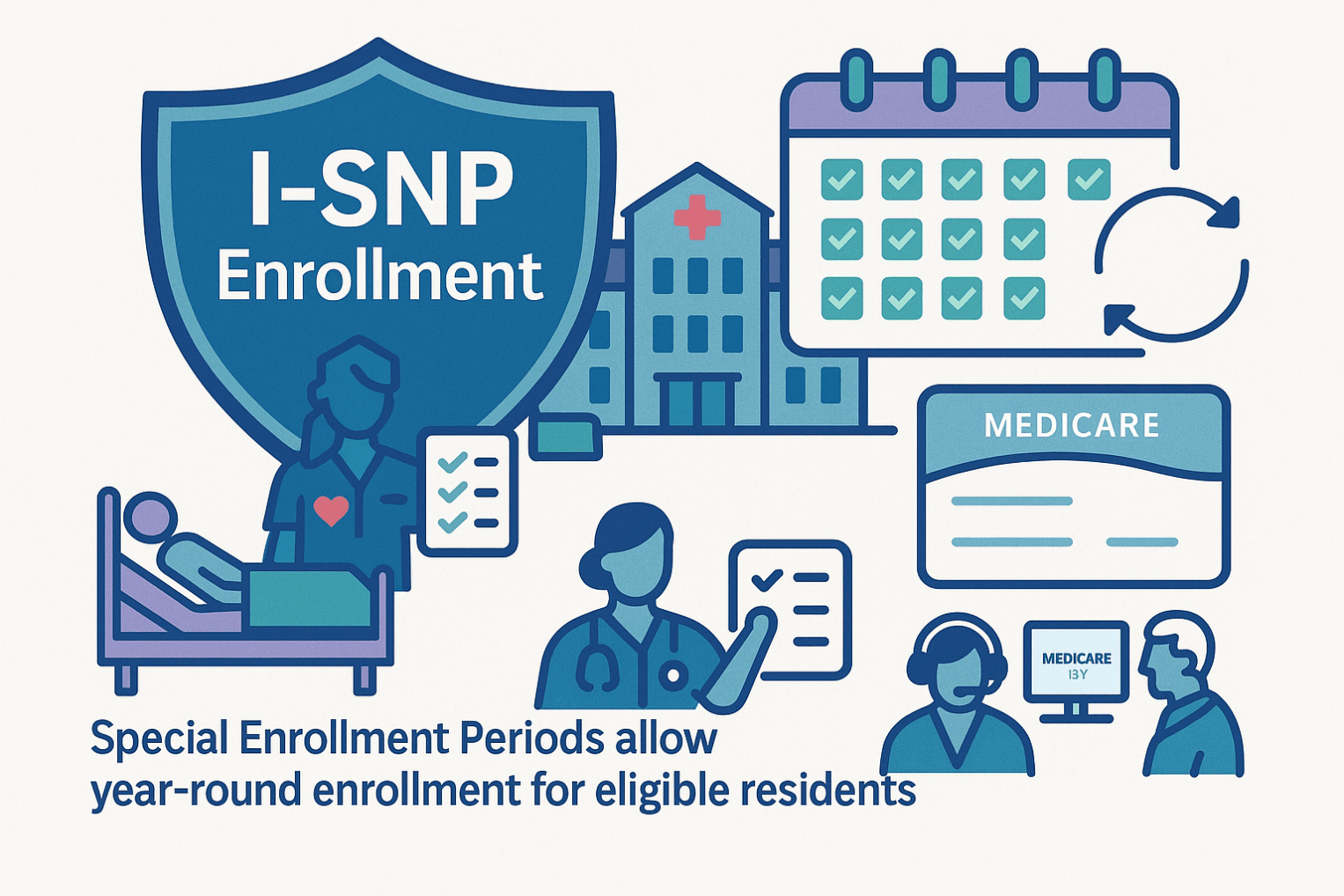
There are three types: C-SNPs for certain chronic conditions (e.g., diabetes, heart failure, COPD, CKD, HIV/AIDS), D-SNPs for people who have both Medicare and Medicaid (dual eligible), and I-SNPs for those living in or needing nursing-home–level care (including qualifying home-based care). SNPs typically feature condition-focused networks, extra benefits (like transportation, dental/vision/hearing, OTC), and lower, more predictable costs. Enrollment is available at standard Medicare periods, and many people qualify for a Special Enrollment Period when they newly meet SNP eligibility.