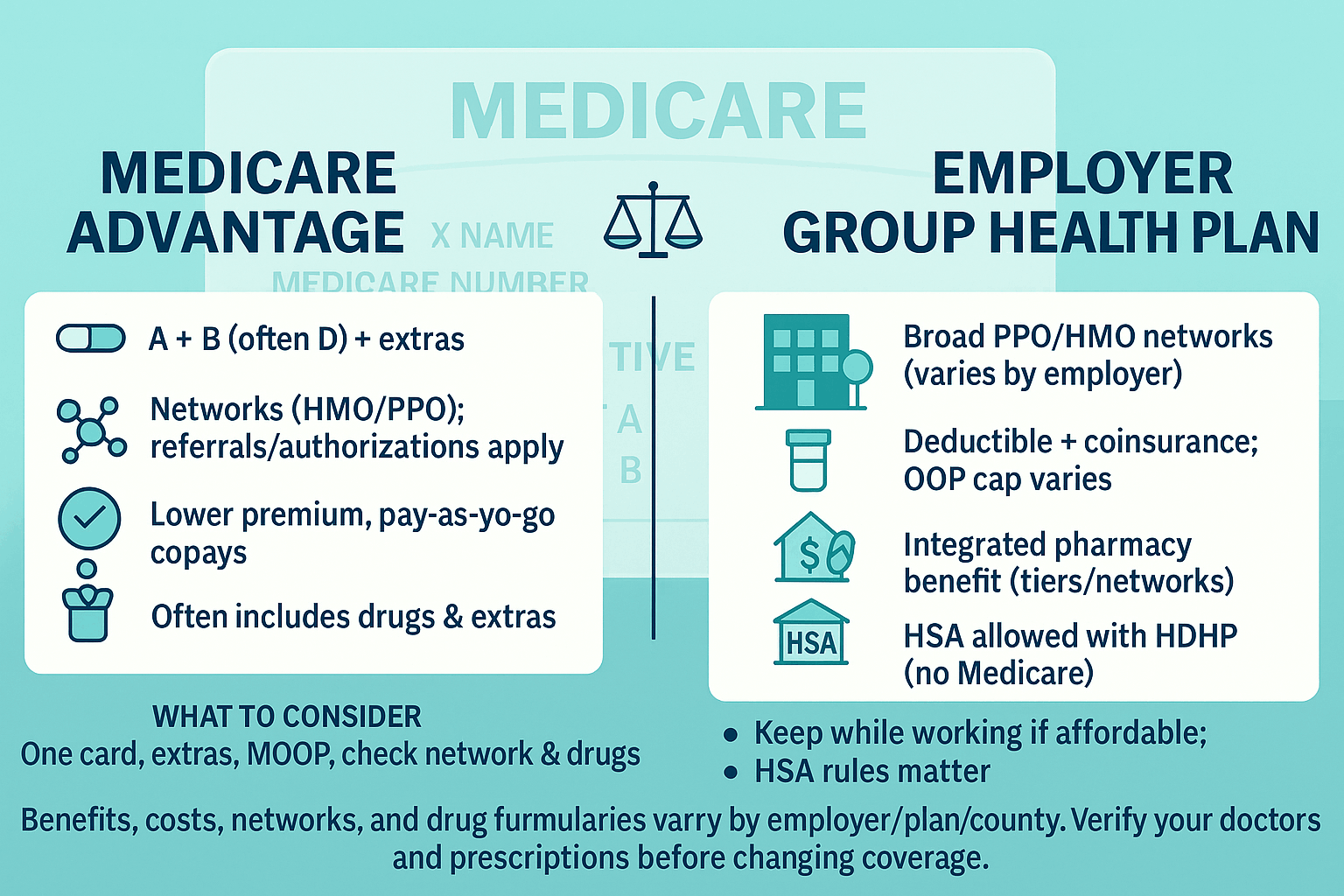
| What it is | Employer/union-sponsored medical plan for active workers and/or retirees (may cover dependents). | Federal program: Part A (Hospital) + Part B (Medical). You can add Part D (drugs) and/or Medigap (Supplement). | Private plan that delivers A & B benefits (often includes Part D) and may add extras. |
| Who runs it | Employer/union (often self-funded) with insurer/TPA; governed by ERISA/plan document. | Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS); uniform national rules for A & B. | Private insurers under CMS contracts; plan benefits/fees approved annually. |
| Eligibility | Set by employer/union (hours, job class, retiree rules). | Age 65+, certain disabilities, ESRD/ALS; must enroll in A/B to use. | Must have Parts A & B, live in plan’s service area, and enroll during a valid window. |
| Primary payer rules (65+) | With active EGHP from an employer ≥20 employees, EGHP is primary, Medicare secondary (if enrolled). With <20, Medicare typically primary. Retiree EGHP is secondary. | When Medicare is primary, providers bill Medicare first; secondary (Medigap/retiree plan) pays after. | MA plan becomes primary for covered A/B services once enrolled (replaces how you receive A & B). |
| Premiums | Employee/retiree contribution varies; employer may subsidize. COBRA is usually full cost (employer + employee + 2% fee). | Part B monthly premium (and Part A premium if not free). Optional Part D premium; Medigap has a separate premium. Higher-income enrollees may owe IRMAA for B/D. | You still pay Part B premium (and IRMAA if applicable); MA plan premium may be $0–low; some areas offer Part B “giveback.” |
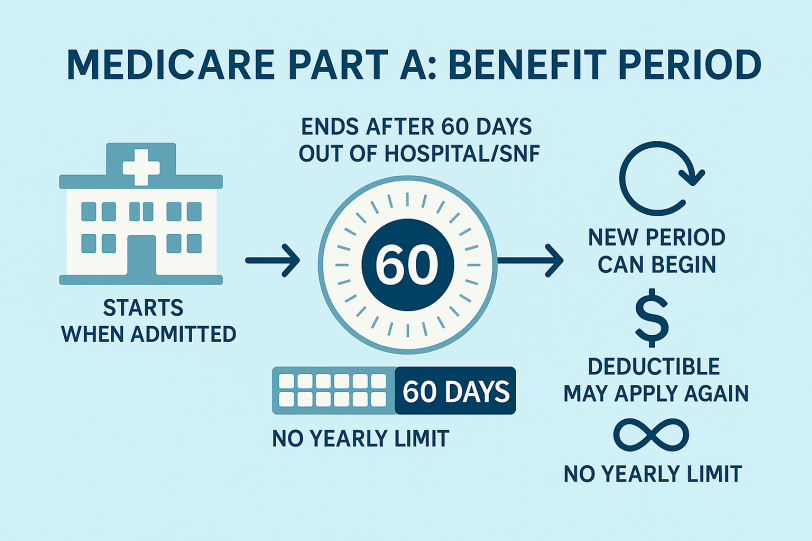
| Deductibles & cost-share | Plan-specific: deductible + copays/coinsurance until plan OOP limit (if applicable). | Part A: per-benefit-period deductible + daily coinsurance for longer hospital/SNF stays. Part B: annual deductible, then typically 20% coinsurance. | Fixed copays/coinsurance by service per plan; structure varies by HMO/PPO. |
| Annual out-of-pocket maximum (medical) | Many large EGHPs include an OOP max (varies by plan). | No MOOP under A & B alone. Many add Medigap to reduce/smooth A/B cost-share. | Yes. Every MA plan has a medical MOOP for A/B services; once met, covered A/B services are $0 for rest of year. |
| Provider access | PPO/HMO/HDHP networks; national employers often broad PPOs; OON rules vary. | Any provider nationwide who accepts Medicare—no networks or referrals. | Networks (HMO, HMO-POS, PPO, PFFS). In-network = lowest cost; OON rules depend on plan type (PPO allows some). |
| Referrals / prior authorization | Common for HMOs and high-cost services (imaging, surgeries, specialty drugs). | Minimal under A/B (some services require auth); no referrals to see specialists. | Common for many services (SNF, home health, imaging, Part B drugs). Referrals often required in HMOs. |
| Prescription drugs | Integrated pharmacy benefit with tiers and preferred pharmacies. | A/B don’t cover most outpatient drugs. Add stand-alone Part D (PDP); costs depend on formulary/tiers/pharmacy. | Often built in (MA-PD). If the MA plan lacks Part D, adding a separate PDP is usually not allowed for HMOs and varies for PPO/PFFS. |
| Extras (dental/vision/hearing, fitness, OTC, rides, meals) | Often included or buy-up options; scope varies widely by employer. | Generally not included with A/B; buy stand-alone DVH if needed. | Frequently included; amounts/networks/maximums vary by plan/county. |
| Supplemental coverage | Not typical (some retiree wraps exist). | Medigap can cover A/B deductibles/coinsurance; no networks; separate premium. | Medigap not allowed with MA (not compatible). |
| Travel / multi-state living | Large national PPOs travel well; HMOs mostly local except emergencies. | Excellent: any Medicare-participating provider nationwide; some Medigap plans include limited foreign travel emergency. | Emergencies/urgent care covered anywhere; routine care tied to network/service area. PPOs may allow some OON nationwide. |
| HSA compatibility | Yes with HSA-qualified HDHP—but only while not enrolled in any part of Medicare. Contributions must stop the month Medicare starts. | No new HSA contributions once enrolled in any part of Medicare (you can still spend existing HSA funds). | Same as Medicare: enrollment ends HSA contributions (spending allowed). |
| COBRA & coordination | COBRA extends EGHP after job loss but is usually secondary to Medicare and does not create the same SEP as active EGHP. | Relying on COBRA while delaying Part B can forfeit SEP and trigger penalties/wait for GEP. | Loss/end of COBRA can create a SEP to join MA/MAPD; watch dates to avoid gaps. |
| Delaying Medicare | With active EGHP from an employer ≥20 employees (yours/spouse’s), you may delay Part B without penalty and use an 8-month SEP after employment / coverage ends. | Many take premium-free Part A at 65 (but this ends HSA contributions). Delay Part B only if you have qualifying active EGHP. | You can enroll in MA once A & B are active; loss of EGHP commonly triggers a SEP to join MA. |
| Enrollment windows | Employer initial eligibility; annual open enrollment; qualifying life events; COBRA timelines. | IEP (7-month window around 65); SEP (e.g., end of active EGHP, move); GEP (Jan 1–Mar 31 if you missed others). Part D aligns; Medigap 6-month OEP when you’re 65+ and Part B active. | ICEP/IEP when new to A & B; AEP (Oct 15–Dec 7); MA OEP (Jan 1–Mar 31 for people already in MA); various SEPs. |
| Typical total-cost pattern | Premium + deductible/coinsurance to plan’s OOP max; drugs integrated. | Part B premium (+ Part A if not free) + cost-share (A/B). Many add Medigap + PDP premiums to reduce variability. | Often $0–low premium; pay copays/coinsurance as used; capped by medical MOOP; drugs included if MA-PD. |
| Best fit (typical) | Active workers with affordable contributions, rich DVH, or HSA goals; some retirees with strong employer subsidy. | People wanting maximum provider freedom and simple national rules; pair with Medigap (predictable costs) and Part D. | People who want one card, potential lower premiums, extras, and a MOOP, and are comfortable with networks/prior auth. |
| Common pitfalls | Assuming COBRA preserves the same SEP as active EGHP; contributing to an HSA after Medicare starts; overlooking out-of-network rules. | Skipping Part D (late penalty); delaying Part B without qualifying EGHP; going without Medigap and facing high A/B exposure. | Not checking doctors/hospitals for network status, formulary/tiers, or prior-auth rules; assuming $0 premium = lowest total cost. |